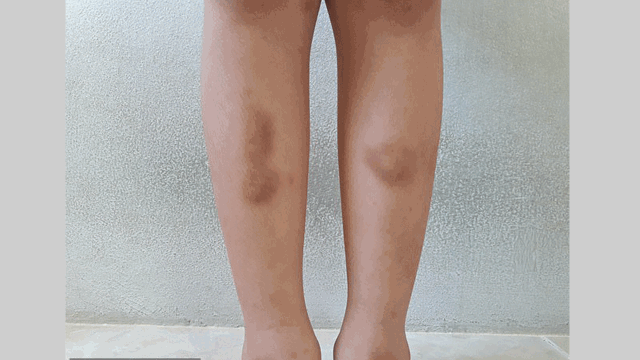
Bruises are common in many individuals and have multiple causes, such as a medication, medical condition, or age.
However, bruises sometimes appear without apparent cause in healthy people. A study of 800 healthy adults showed that 18% had bruises without injury or collision with a hard surface.
The bruising develops in 3 steps beginning with small blood vessels called capillaries that are damaged and exploding. The leakage of blood that collects under the skin leads to the appearance of platelets, which are small cells in the blood that float to the surface of the subcutaneous infection called thrombus or thrombosis and strengthen proteins called coagulation factors.
Bruising without cause is common. Some medications may be caused by platelet abnormalities and, in some cases, by garlic, while liver disease or vitamin K deficiency is a cause of bruising.
The appearance of bruising increases with age, or in women who have light skin, or who are overweight, for no apparent reason.
Drugs that can cause ibuprofen bruises, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, anticoagulants (such as warfarin), antiplatelet drugs (such as aspirin and clopidogrel) and steroids (such as prednisolone).
Bruising is not a concern, and there is no cure for bruises that appear without direct causes of external factors, except in the avoidance of their internal causes.