The commissioning of new spacecraft will significantly increase the capabilities of the Russian constellation of the GLONASS navigation system.
This was reported to journalists by the head of the test department of the Main Test Space Center named after G.S.
Titov Lieutenant Colonel Alexander Grebenyuk.
According to the officer, currently the orbital constellation of the GLONASS system includes 26 spacecraft, three of them belong to the new type GLONASS-K, the rest belong to the GLONASS-M series.
As Grebenyuk explained, GLONASS-K differs from its predecessor in multifunctionality, higher performance characteristics and a ten-year guaranteed service life (GLONASS-M has seven years).
In the future, the number of these satellites will increase significantly.
“In the future, launches of GLONASS-K devices will make it possible to increase the accuracy characteristics of the group (Russian navigation satellites. -
RT
) by an order of magnitude, as well as increase its service life,” Grebenyuk said during a press tour dedicated to the Day of the Russian Space Forces, which celebrated October 4th.
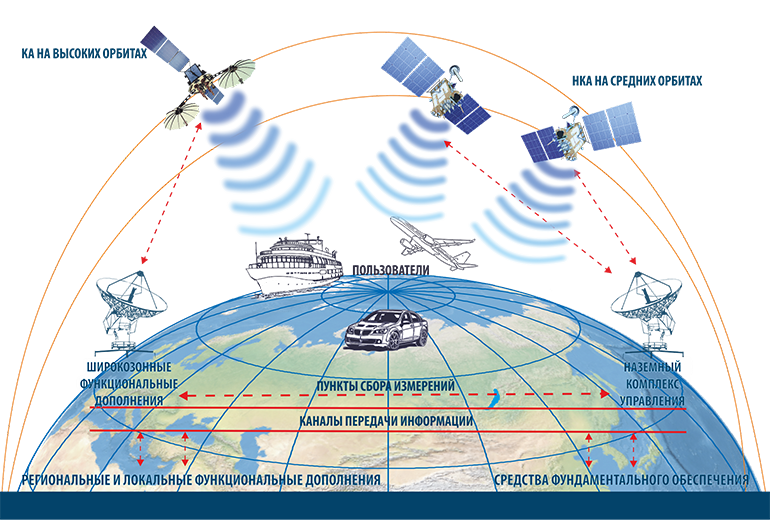
As the officer said, the devices of the Russian global navigation satellite system are located in three orbital planes.
Such a construction provides global coverage of the earth's surface and near-Earth space by the navigation field at altitudes up to 2 thousand km.
Scheme of functioning of the GLONASS system
© GLONASS User Information Center
The main developer of satellites for GLONASS is located in the Krasnoyarsk Territory JSC Information Satellite Systems.
Academician M.F.
Reshetnev" (ISS).
The launch of domestic navigation satellites into orbit is carried out by the Soyuz-2.1b medium-class space rocket (RKN).
The Fregat apparatus is used as an upper stage, capable of performing all the necessary operations without interference from the Earth.
Comparable to GPS
A feature of GLONASS is that the system allows an unlimited number of consumers, regardless of weather conditions, to determine their coordinates and speed anywhere in the world.
GLONASS began to be created in the mid-1970s to accurately and quickly determine the location and speed of physical objects on the ground, in the air and in space.
The first apparatus of this system, Cosmos-1413, went into orbit in 1982.
Initially, the GLONASS system was conceived as a military space system, but over time it has found wide application in civilian areas.
Among the mass consumers are road, air, sea transport.
With regard to the Armed Forces of the Russian Federation, the stable operation of GLONASS allows the use of high-precision weapons, solving the problems of topographic and geodetic support, naval navigation and target designation.
In an interview with RT, a military expert, retired colonel Mikhail Khodarenok, said that without the grouping of GLONASS devices, the Russian Armed Forces could not be called a modern army.
“Any modern army should have a global positioning system.
The importance of GLONASS is exceptionally great.
Suffice it to say that thanks to this system, Russia can use sea and air-based cruise missiles with high accuracy, ”Khodarenok emphasized.
Preparation for the launch of a new generation satellite for the GLONASS system
© JSC "Information satellite systems" named after academician M. F. Reshetnev"
In a RT commentary, military expert Yuri Knutov noted that GLONASS allows you to determine the coordinates of the carrier of guided weapons and enemy positions to be destroyed.
According to the analyst, without the navigation system, the RF Armed Forces would not be able to use such missiles as Caliber, Onyx, Kinzhal and other guided munitions with the necessary accuracy.
An important milestone in the modern history of GLONASS was the adoption in 2001 by the government of the Russian Federation of the federal target program (FTP) "Global Navigation System".
It is this type of satellite that now forms the basis of the grouping of the navigation system.
Also, during the implementation of the FTP, the ground control complex was upgraded.
These activities made it possible to increase the accuracy characteristics of GLONASS to a level that allows it to compete with foreign global navigation systems, including the American GPS, the center named after G.S.
Titov.
The mass of GLONASS-M is 1415 kg, the power of the power supply system (PSS) is 1400 watts.
The device is equipped with a domestic on-board digital computer (TsVM).
Compared with satellites of the previous generation, the accuracy of determining the location of objects in these satellites is increased by 2.5 times.
"GLONASS-K" is lighter than "GLONASS-M" by almost half a ton with a power supply system of 1460 watts.
According to experts, the radical reduction in the mass of the satellite allows us to conclude that GLONASS-K has more advanced on-board systems and digital computers.
Management sessions
The control center of the GLONASS system is located in Krasnoznamensk near Moscow.
It is from here that the combat crews of the center to them.
Titov (a structure of the 15th Army of the Aerospace Forces of the Russian Federation), round-the-clock and continuous control of the entire group of GLONASS devices is carried out.
Approximately 300 management sessions are performed daily.
One of the main tasks of the military personnel of the center.
Titov - monitoring the technical condition of satellites.
“The state of the onboard equipment of the GLONASS spacecraft is assessed based on the analysis of the received telemetric information containing the values of all controlled parameters, the deviation from the norm of which can lead to a malfunction of the spacecraft,” said Alexander Grebenyuk.
The work of the military personnel of the center.
Titov
As the officer explained, the elimination of emergency situations is carried out by combat crews with the involvement of operational groups, which include specialists from enterprises that develop elements of spacecraft.
In the most difficult situations, combat crews together with representatives of the chief designer of the ISS them.
Reshetnev develop non-standard solutions to eliminate the problems that have arisen.
As told to reporters in the center.
Titov, during the operation of the GLONASS-M series devices, there were facts of damage to the body of spacecraft by space debris and celestial bodies, that is, physical objects of natural origin.
As a result, the satellites were depressurized, and they lost their functionality.
The use of leaky platforms in the creation of new spacecraft of the GLONASS-K series made it possible to eliminate the occurrence of these malfunctions, explained in the center.
Titov.
“Most often, we observe minor malfunctions that are quickly eliminated through control commands from the ground.
As a result, the device continues to work within the specified functionality,” said Grebenyuk.
According to the lieutenant colonel, a very serious reliability resource is being laid into the spacecraft of the GLONASS system.
Existing control algorithms implemented in special software make it possible to almost always launch a backup system in the event of a failure of one system.
“In addition, each spacecraft has a self-control system.
Thus, after self-diagnosis, in case of deviation of the operating parameters, it can independently switch to another set of equipment in order to maintain a healthy state.
If the device fails to solve the problems that have arisen on its own, then it sends an appropriate signal to Earth, ”says Grebenyuk.
With high precision
The immediate plans of the Aerospace Forces include the creation of a new ground control complex (GCC) for a group of GLONASS satellites.
Work on its creation should be completed by 2027.
“In addition to the control facilities located on the territory of Russia, the new ground control complex (GCC) will also include stations in Antarctica.
In addition, the new NKU will allow for interaction with Roscosmos measuring stations, the website of the Russian Defense Ministry says.
According to Yuri Knutov, the Russian Ministry of Defense directs significant resources to maintain the stable operation of GLONASS and the development of this system.
Such a policy, according to the expert, brings tangible practical results.
At the GLONASS system command post (Titov Center)
RIA News
© Sergey Pyatakov
“The undoubted advantage of GLONASS satellites is high noise immunity, resistance to various electromagnetic pulses, solar flares, and the likely effects of electronic warfare (electronic warfare. -
RT
).
With the commissioning of a new generation of satellites, the accuracy and reliability of GLONASS will reach a higher level,” says Knutov.
In an interview with RT, Nathan Eismont, a leading researcher at the Space Research Institute of the Russian Academy of Sciences, said that the further improvement of GLONASS is of great importance not only for Russia's defense capability, but also for our country's economy.
“Now the accuracy of GLONASS is approximately at the level of other similar systems - American GPS, European Galileo, Chinese BeiDou.
They can determine coordinates with an accuracy of about a meter or less.
Such accuracy is needed not only by the military, it is also important for the normal operation of land and sea transport, tracking seismic processes, ”Eismont emphasized.