Why does the brain need rest?
After how many minutes of deep thought you should take a break?
What is the difference between the cerebrum and the cerebellum?
What are the warning signs of a clot in the body that may travel to the brain and cause a stroke?
The answers are in this report, along with advice on regular tests that are important for your brain and body health.
Why do our brains need periods of rest?
The answer is that the brain needs regular rest periods to get rid of metabolic waste, and it is designed to function in cycles such as the circadian rhythm through wake and sleep schedules.
And a report by the French newspaper “Le Figaro” quoted Michel Le Van Quinn, director of research at the National Institute of Health and Medical Research, author of “The Brain and Silence: The Keys to Creativity, Serenity, Mind and Nature,” that “the brain cannot work more than 10 minutes on a task.” It requires a lot of concentration, and he needs a break before starting over."
After how many minutes of deep thought should you take a break?
Human attention decreases after about 10 minutes of intense mental work without taking a break, due to the fact that noise pollution and other distractions such as emails, SMS, calls, etc., stimulate the sympathetic nervous system.
Michel Le Van Coen explained that when the sympathetic nervous system is stressed, this results in increased secretion of stress hormones, including norepinephrine.
When taken in small doses, norepinephrine improves brain activity, specifically the interaction between neurons in the frontal lobe, but when it is in high doses, other receptors are activated that inhibit neuronal activity.
The activity of the frontal lobe, the center of executive functions, thus slows down, causing stress that impairs the ability to focus.
Gloria Mark, a professor of computer science and a researcher at the University of California, said that working on a screen in a noisy environment such as open space undermines attention with an intermittent task every 11 minutes on average, and it takes the brain 23 minutes to regain focus and return to its task.
The amygdala reacts a lot to the unexpected and noise, and the sense organs usually send its information to the thalamus and neocortex for interpretation there.
But about 10% of the information gets straight to the amygdala, which reacts very quickly to specific sensory information without even analyzing what's going on.
This is not without consequences, because an overactive amygdala constantly stimulates the sympathetic system and increases norepinephrine production, affecting concentration.
In fact, the MRI of the brain of people who live in cities is different from those who live in a quiet environment.
And a study conducted on the impact of social stress in Germany and Canada established that "the amygdala in those who live in cities is more sensitive."
Regeneration mechanisms in the brain
The brain prepares the mechanisms of renewal during moments of rest and sleep, and the glial cells responsible for feeding and protecting the neurons carry out the task of eliminating their waste, that is, the remains of metabolic reactions that occur in the brain in particular to nourish the neurons that consume a lot of energy, and the cleansing system is called the glymphatic system system).
This device is essential because the accumulation of brain waste increases the risk of developing neurodegenerative diseases, such as Alzheimer's and Parkinson's.
"Puting mice in a quiet environment generates a much higher number of neurons in the brain structure, compared to exposure to different sounds," says Michel Le Van Coen.
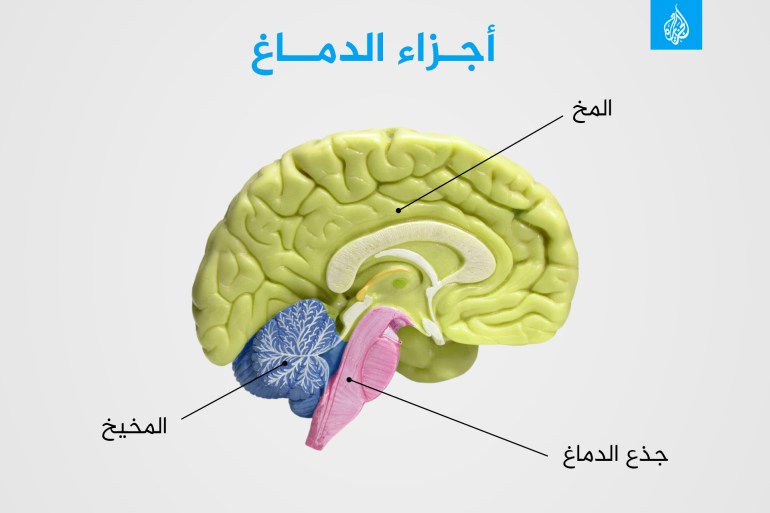
What is the brain?
The brain is part of the central nervous system, and it includes various structures.
A report published by the Spanish website medicoplus stated that the central nervous system is responsible for controlling everything that happens in the body, including: looking, speaking, walking, jumping, running, breathing, reading, thinking, imagining, and smelling. .
Although we do not know many things about this organ, we also know a lot about it, such as its anatomical shape.
The brain and spinal cord are the main components of the central nervous system, and the brain includes different structures, including the cerebrum and the cerebellum, and each has its own functions.
The brain is protected by the bones of the skull, where the organization and interconnection of neurons is of the utmost complexity.
It represents the body's true control center, interprets information from outside and inside, and generates responses and commands.
The brain, in turn, consists of 3 main structures:
The brain (cerebrum).
Cerebellum (cerebellum).
The brainstem that regulates vital functions and allows connection to the spinal cord.
What is the brain?
The cerebrum is the largest part of the brain, accounts for 85% of its weight, occupies the upper part of it, and is divided into two halves.
It is responsible for controlling muscle movements, synthesis of hormones, development of emotions and feelings, storage of memories, memorization and learning.
The brain is the structure of the brain that receives stimuli from the senses, interferes with vital functions, and allows us to communicate with the outside world, meaning that it is responsible for everything related to thinking and movement.
The brain weighs between 1300 and 1500 grams, and the cerebral cortex is divided into two halves (left and right), each of which has 4 lobes:
The frontal lobe
The frontal lobe is the largest and one of the most developed areas of the brain. It is responsible for controlling muscle movements, memory, learning, impulse suppression, planning, stimulating emotional intelligence, language, problem solving, and processing olfactory information.
The parietal lobe
Located in the upper back of the brain, the parietal lobe integrates sensory information, processes pain, causes us to locate in space, develops mathematical reasoning, permits verbal language, controls the urinary sphincter, enhances memory, develops manual skills and maintains Healthy mood.
temporal lobe
The temporal lobe, located in the lower lateral region of the brain, processes auditory information, helps us understand language, processes visual information, allows us to associate written words with sounds, associate letter heights with sounds, stimulates space perception and the ability to orient our bodies toward sound, enhances Memory and attention span, relates perceptions and emotions and stores auditory and visual information.
occipital lobe
The occipital lobe is the smallest of the four. It occupies a lower posterior position. It receives nerve impulses from the eye, processes visual information, stimulates memory, interprets images, stimulates thoughts and emotions, distinguishes colors, captures movement, and allows recognition of space.
The brain consists of other areas, such as:
The hypothalamus region.
The amygdala (amygdala).
Hippocampus (hippocampus).
The thalamus (thalamus).
What is the cerebellum?
The cerebellum is a small part of the brain that accounts for 10% of its total weight. It is located at the back of the skull and the lower part - that is, the bottom of the brain - and its main function is to integrate sensory information and motor commands generated by the brain.
The cerebellum is responsible for making sure that our voluntary movements are coordinated correctly and that they happen at the right time. It is also known as the 'little brain'.
The cerebellum controls bodily functions such as balance and coordination and acts as a physiological regulator of tremor.
The common belief was that the cerebellum's sole function is related to controlling the motor commands sent by the brain to the musculoskeletal system, but recent studies indicate that it can be linked to cognitive functions such as perceiving music, learning, attention, language, and sometimes memory.
The cerebellum is attached to the posterior wall of the brainstem, has an approximate weight of 150 grams, has a flat-conical shape, and is divided into 3 lobes: anterior lobe, posterior lobe and nodular lobe.
5 differences between the cerebrum and the cerebellum
The cerebrum is larger than the cerebellum
The cerebrum represents 85% of the brain's weight, compared to only 10% for the cerebellum.
The weight of the brain in adults ranges between 1300 and 1500 grams, in contrast, the weight of the cerebellum does not exceed 150 grams.
cerebellum under cerebellum
One of the best ways to distinguish between the two is their location within the skull, since the cerebrum is located at the top of the brain while the cerebellum is located below, and is connected to the brainstem.
The brain has four lobes and the cerebellum has three
The cerebrum and cerebellum are divided into two halves, but they have a different number of lobes. The cerebrum is divided into 4 lobes (frontal, parietal, temporal and occipital), while the cerebellum is divided into 3 (anterior, posterior and nodular).
The brain plans the movement of the muscles and the cerebellum coordinates them
The most important differences between the cerebrum and the cerebellum lie in the functions. The cerebrum is responsible for planning movements, controlling body physiology, and synthesising hormones.
The functions of the cerebellum are no less important, but they are less comprehensive, as its role is limited to coordinating the motor commands sent by the brain to the musculoskeletal system, thus ensuring correct movement, coordination and balance.
Cognitive functions are more closely related to the brain
Functions such as reasoning, ideas, learning, memory, emotions, imagination, integration, processing sensory information, and speech are all linked to the brain.
Although recent research suggests that the cerebellum may also be involved in some of these functions (music, learning, attention, language, and sometimes memory), the general rule is that the cerebellum's role is limited to coordinating muscular commands.
Signs that warn you of a blood clot that may cause a stroke
There are early warnings that the body may send when a blood clot occurs, and when a clot occurs, it may travel anywhere in the body, causing a heart attack if it blocks an artery in the heart, or a stroke if it blocks an artery in the brain.
A report by the Turkish "Sabah" website indicated that despite it being a common disease, the number of people dying as a result of diseases caused by blood clots is increasing, attributing the reason to the delay in noticing the presence of the condition or perhaps not noticing it at all.
The report shows that there are signs or warnings that may help in the diagnosis and early observation of clotting and blood clotting, pointing out that there are measures we can take, foremost of which is raising the level of awareness and awareness of this serious problem, because the body already gives advance signals, and people have to realize this and go to the doctor;
Especially women, as the damaged blood vessels condense the blood at a certain point to prevent its flow, causing a clot, and thus the blood will not be able to go beyond the clotted area.
The newspaper reviewed these are the signs that may indicate the occurrence of clotting, which are:
swollen feet
The most common place for blood to clot is the foot, where its flow is interrupted, which may cause swelling, and the foot becomes red.
leg pain
Deep vein thrombosis can also be felt in both the leg and the foot, causing pain when touching the leg.
pain in chest
If you have a lung clot, you should see a doctor right away.
One of the symptoms that indicates the occurrence of this clot is the feeling of a needle prick in your chest, and you may feel sharp pain in the chest or back, but the difference between it and other chest pains is that you will feel pressure in your chest.
Difficulty breathing
If you're having trouble breathing, don't take it lightly;
When you have difficulty breathing, your heart is beating too fast, you get cold sweats, feel dizzy or faint, you may have a lung clot, and if you have all of the symptoms listed above, don't ignore it and see your doctor right away.
dry cough
If you are not sick and are coughing constantly, pay attention to other signs, you may have a lung clot;
The most common accompanying symptoms are: heart palpitations, chest pain, difficulty breathing, and in rare cases, bloody sputum may result.
Vomiting and diarrhea
If a clot forms in your intestines, you will feel severe stomach pain. The most common symptoms here are headache, vomiting and bloody diarrhea.
Severe headache
A blood clot in the brain can lead to a stroke. The headaches are caused by not enough oxygen reaching the brain. You may also find it difficult to see or speak.
4 important blood tests
We conclude with a set of important tests for the health of the body, including the brain:
cholesterol test
It is recommended to conduct a blood cholesterol level analysis periodically, and this will prevent you from several cardiovascular diseases, including high blood pressure, stroke and stroke, according to a report published by the Indian “Healthshots” website.
Sugar analysis
Symptoms that suggest diabetes, such as extreme thirst, blurry vision, frequent urination, increased hunger, numbness or tingling in the feet, tiredness, and sudden weight loss or gain.
Therefore, it is necessary to conduct a periodic blood sugar analysis for early detection of any underlying disease.
Iron analysis and complete blood count
The most prominent symptoms of iron deficiency and red blood cells are weakness, fatigue, fever, inflammation, and bruising or bleeding.
If these symptoms appear on you, this analysis must be done as soon as possible.
Thyroid
If you suffer from anxiety, irritability, nervousness, trouble sleeping or losing weight, a thyroid test is a must, as thyroid problems are very common these days.