What is a urinary tract infection?
And what are its symptoms?
And what is its treatment?
Does it cause dizziness?
Does it lead to death?
And how can reduce the risk of infection after intercourse?
What is a urinary tract infection?
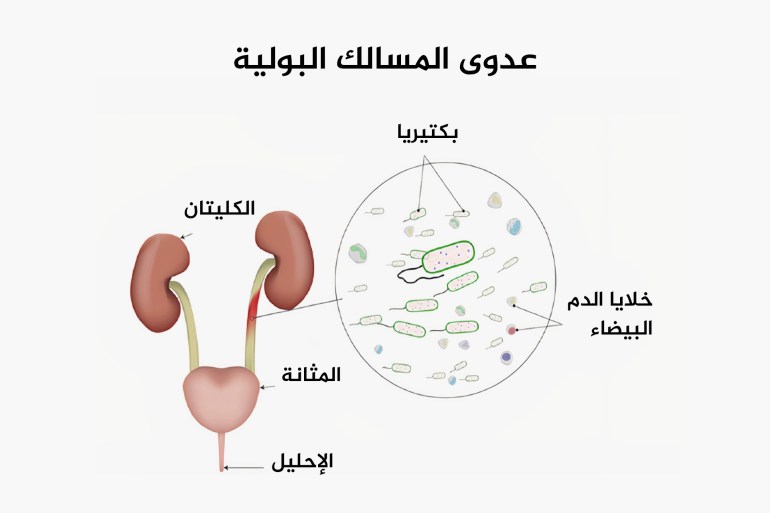
Urinary Tract Infection is an infection of the urinary system. This type of infection can include the urethra (a condition called urethritis), the kidneys (a condition called pyelonephritis), or the bladder (a condition called cystitis). That's according to the Cleveland Clinic.
Urinary tract infections are caused by microorganisms - usually bacteria - that enter the urethra and bladder (Sidra Medicine)
What is the cause of inflammation in the urine?
Your urine usually does not contain bacteria (germs), it is a byproduct of our 'kidneys' filtering system. When waste products and extra water are removed from the blood by the kidneys, urine is formed that travels through your urinary system without any contamination. However, bacteria can enter into the urinary system from outside the body, causing a urinary tract infection.
Urinary tract infection causes
Urinary tract infections are caused by microorganisms - usually bacteria - that enter the urethra and bladder causing inflammation and infection. Although this infection most commonly occurs in this area, the bacteria can also travel through the ureters and infect the kidneys.
More than 90% of bladder infections are caused by Escherichia coli (E. coli), a bacteria normally found in the intestines.
Urinary tract infection symptoms
A urinary tract infection causes its lining to become red and irritated, which can lead to some of the following symptoms:
Pain in the flank, abdomen or pelvic area.
pressure in the lower pelvis.
Frequent need to urinate.
incontinence.
painful urination;
Presence of blood in the urine.
The need to urinate at night.
Abnormal urine color (turbid).
Strong or foul-smelling urine.
Other symptoms that may be associated with a UTI include:
Pain during intercourse.
Penile pain.
Fatigue.
Fever (temperature above 37.8°C) and chills.
vomiting;
Mental changes or confusion.
Does urinary tract infection cause dizziness?
Urinary tract infection - especially severe - may lead to fatigue, and also can lead - especially in the elderly - to low blood pressure that may cause dizziness, and severe infection can also cause muscle weakness, leading to the inability to stand without assistance, and this It may lead to a fall in the elderly.
Urinary tract infection and sexual intercourse
“During intercourse, pushing can introduce bacteria into the urethra and bladder, increasing the risk of UTIs,” says Dr. Lakisha Richardson, obstetrician and gynecologist.
According to a 2013 review, UTIs are likely to affect at least 50 to 60% of women in their lifetime, and although men are less likely to get this infection - especially after intercourse - it can still occur, according to a report In the Health Line.
Urinary tract infection can occur as a result of intercourse, especially women, and the reason that women are more likely to contract this infection than men is due to the female anatomy, as their urethra is shorter than men, which means that it is easier for bacteria to reach the bladder, and the urinary tract is shorter than that of men. The urine is closer to the anus in women, which makes it easier for bacteria such as Escherichia coli to reach the urethra.
Although anyone is at risk of developing a urinary tract infection after intercourse, Richardson says that women with a history of recurrent urinary tract infections or abnormalities are more likely to get this infection.
How can you reduce the risk of developing a urinary tract infection after intercourse?
One helpful tip is to always urinate after sex, says Richardson. "Removing any bacteria in the bladder after sex reduces the risk of a UTI," she explains.
Some doctors also recommend urinating before sex, to reduce the risk of UTIs.
Washing the genital area with warm water before sex may reduce the risk of bacteria entering the urethra, especially in women.
Certain contraceptives, such as diaphragms or spermicides, may increase the risk of UTIs. If you think either of these things may be contributing to a UTI, consider other forms of contraception.
Richardson also says that women with recurrent urinary tract infections may benefit from taking a prescribed antibiotic after sex, usually a single dose taken immediately after intercourse.
How is a urinary tract infection treated?
To treat a UTI, you will need antibiotics, which are medicines that kill bacteria and fight infection. Your healthcare provider will choose the medicine that is best to treat the specific bacteria causing it. Some commonly used antibiotics can include:
Nitrofurantoin (Nitrofurantoin).
Sulfonamides
Amoxicillin (Amoxicillin).
Cephalosporins.
Trimethoprim/sulfamethoxazole (Trimethoprim/sulfamethoxazole).
Doxycycline.
Quinolones.
It is very important that you follow your healthcare provider's directions for taking the medication, and you should continue to take it for as long as your doctor recommends. Do not stop taking the antibiotic just because your symptoms are gone and you are starting to feel better, because if the infection is not completely treated, it may return.
Best antibiotic for urinary tract infection
There is no better antibiotic, for each case and each patient is specific, and requires treatment that suits his condition.
Is urinary tract infection a serious disease?
Urinary tract infection can be easily treated with antibiotics, but if it is not treated or if you stop taking the medication early, this type of infection can lead to something more serious, such as a kidney infection.
Call your healthcare provider if you have symptoms of a UTI. If your symptoms get worse, you may need a different treatment. Watch out for these in particular:
fever.
Back pain.
vomiting;
If you have any of these symptoms or other symptoms persist after treatment, contact your healthcare provider. UTIs can spread throughout the urinary tract and to other parts of the body, however treatment is very effective and can relieve symptoms quickly.
Does urinary tract infection lead to death?
Untreated UTIs and spreads can lead to a condition called urosepsis, which occurs when an untreated UTI spreads to your kidneys. It's a form of sepsis, your body's response to a life-threatening infection.
Urinary tract infection can be fatal if not treated properly, according to a report in WebMD.
Is there a relationship between urinary tract infection and prostate cancer?
There is not enough data yet to say there is a relationship, but there is a study published in 2017 in the journal "PLOS One", and researchers found that cystitis or urethritis may play a role in the development of prostate cancer in Taiwanese men, especially in those who visit the doctor frequently because of this.
The researchers called for more studies to be conducted in other countries, particularly where the prevalence of prostate cancer is high.
A recent study, reported by the French newspaper Le Point and the British Guardian newspaper, identified a bacteria potentially linked to prostate cancer.
Researchers at the University of East Anglia in England conducted precise genetic analyzes on urine and prostate tissue of more than 600 men, whether they had this disease or not, and at the conclusion of their study, they said they found 5 types of bacteria associated with the rapid progression of the disease.
Although the study is currently unable to prove that the bacteria cause or exacerbate prostate cancer, but if ongoing work confirms the role of these bacteria, researchers will be able to develop tests to identify men most at risk, and possibly find antibiotics to prevent this disease.