The National Health Service in Britain, "NHS" (NHS) has started a trial of 1,000 diabetic patients using artificial pancreas devices, so how does this device work?
What is the significance of this scientific breakthrough?
The news was published by "The BMJ" medical journal, and "The Times" and "Daily Mail" newspapers.
How does an artificial pancreas work?
The NHS trial, made by Medtronic, is the world's first certified closed-loop insulin delivery system, the Times reports.
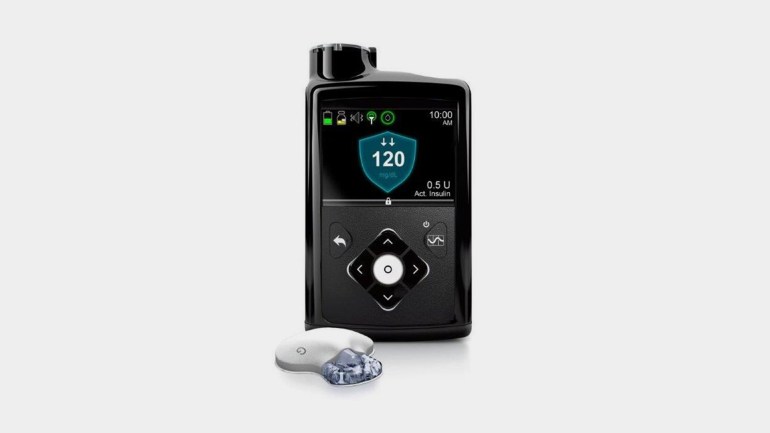
The artificial pancreas injects the body with insulin as needed from a pump carried by the patient, as it sends readings to a smart device that calculates the required amount of insulin, and then tells the pump how much should be excreted into the blood.
The system will constantly monitor blood sugar levels and automatically adjust the amount of insulin given through a pump.
"100 years after the discovery of insulin, the artificial pancreas is a potentially revolutionary development in the treatment of diabetes," said Professor Partha Carr, diabetes specialist advisor at NHS.
The trial will involve about 1,000 patients from about 25 diabetes centers in England.
The results of this experiment will be used by the National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (Nice), as the institute is studying whether NHS adoption of the technology will be effective or not.
The trial participants are expected to be patients who already use an insulin pump and carry glucose monitors, but who still struggle to keep their blood sugar levels under control.
Doctors hope the artificial pancreas will help:
Preventing life-threatening episodes of hypoglycaemia.
Facilitate blood sugar control.
Simplify patients' lives by eliminating the need for fingerstick glucose testing.
"Living with diabetes is a daily challenge for millions of people, and this closed-loop technology enables them to make a significant difference in their lives," said Sir Simon Stevens, chief executive of NHS England.
The closed-loop system is an automated control system that organizes one or more processes or mechanisms, based on the information received, and in the case of an artificial pancreas, the device secretes insulin to the body according to the information received from blood sugar measurements.
What is type 1 diabetes?
Type 1 diabetes occurs when the pancreas does not produce insulin, because the immune system attacks and destroys the insulin-producing beta cells of the pancreas.
It is also called insulin-dependent diabetes and juvenile diabetes.
Insulin is the hormone produced by the beta cells of the pancreas, and it is essential in the metabolism process, as it supplies the cells with glucose through the blood, after the glucose is extracted from food that is digested and absorbed in the gut.
The lack or loss of the hormone insulin in the body leads to two problems, the first is that the cells do not get the energy they need, and the second is that glucose accumulates in the blood and its levels rise, which results in damage to the body such as weak nerve sensation, kidney failure, heart diseases, and arteries.
Type 1 diabetes is classified as an autoimmune disease, as the immune system protects the human body by recognizing foreign bodies such as bacteria and viruses, and then attacking and destroying them, and also protects it from the abnormal growth of cells that leads to cancer, as the immune system By attacking the cells of the body that had mutations that made them turn cancerous and destroying them.
People with type 1 diabetes cannot produce enough insulin and need daily doses of the hormone to keep blood sugar levels under control, delivered via an injection pen or pump.
Before insulin was discovered in 1921, people with type 1 diabetes rarely lived longer than a year or two.
What is low blood sugar?
Low blood sugar (low blood glucose) A condition that occurs when the level of glucose in the body drops, and sugar is considered low if it is less than 70 milligrams per deciliter in the blood, as a decrease in sugar to this limit or less may harm the body.
Healthy people may develop hypoglycemia as a result of extreme hunger and great physical exertion, but it is more common in diabetics.
When the blood sugar level drops, glucose levels become insufficient to supply the body with the energy needed to perform various activities.
A drop in blood sugar usually occurs as a side effect or complication resulting from diabetes treatment, as a result of several factors: the most important of which is if the patient took an overdose of medication, neglected one of the meals, or as a result of excessive physical activity.
The artificial pancreas constantly monitors blood sugar levels and automatically adjusts the amount of insulin given (communication sites)
Symptoms of low blood sugar include:
shivering feeling
Extreme hunger.
increased sweating;
Rapid heartbeat.
Vertigo.
Lack of focus.
nervousness;
Uncommon strange behaviour.
If symptoms are not dealt with, it may develop into more serious symptoms, which are nervous convulsions and loss of consciousness.
In some cases, severe hypoglycemia may lead to death.