How is Tianwen No. 1 recently?
What are you doing?
How is Tianwen No. 1 recently?
What are you doing?
The reporter learned from the National Space Administration and China Aerospace Science and Technology Corporation that the Tianwen-1 probe has been in orbit for more than a month.
The period of the parked orbit is two Martian days (49.2 hours).
Only a small amount of orbit maintenance is required during the mooring orbit operation to ensure that the probe can conduct a detailed inspection of the scheduled landing area every two Martian days.
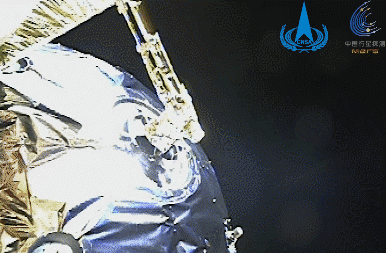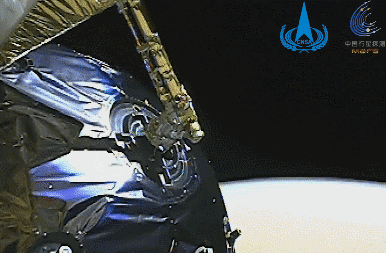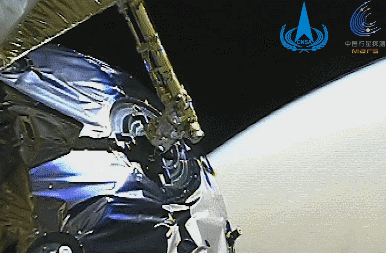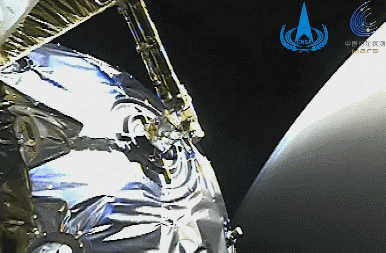
This is the flight image of my country's first Mars exploration mission, Tianwen-1, issued by the National Space Administration.
Issued by Xinhua News Agency (Photo courtesy of China National Space Administration)
The main purpose of running on the moored orbit is to prepare for landing.
During the parking orbit operation, when the detector passes over the scheduled landing area, it will use medium-resolution cameras, high-resolution cameras, spectrometers and other load equipment to conduct detailed inspections of the scheduled landing areas, mainly to detect the topography, geology, and geology of the scheduled landing areas. The topography and whether there are environmental conditions such as sandstorms, etc., make preparations for the safe landing of the landing patrol.
The scrutiny work requires the probe to fly as much as possible over the intended landing zone.
Image of the Mars capture process of the Tianwen No. 1 rover (picture from a directional antenna surveillance camera)
After the Tianwen-1 rover arrived on Mars, it carried out a series of complex orbit changes.
On February 10, 2021, the probe carried out capture and braking when it first reached the near-fire point, and successfully realized Mars orbit, entering a large elliptical orbit with a period of 10 days; on February 15, the probe reached the far-fire point for the first time The orbit change was carried out at the point of ignition, and the orbital plane and the height of the near-fire point were adjusted. The orbit of the circular fire became a polar orbit passing through the north and south poles of Mars. It is a four-day phase modulation orbit, so that it can pass just over the scheduled landing zone when it reaches the near-fire point again in one revolution.
Although the probe was already above the scheduled landing zone when it reached the near-fire point for the third time, due to the rotation of Mars, it would be difficult for the probe to fly through the scheduled landing zone again for a long time without an orbit adjustment.
Therefore, it is necessary to perform another near-fire braking and enter the parking track so that the detector can fly over the scheduled landing zone every time it returns to the vicinity of the near-fire point.
On February 24, when the Tianwen 1 Mars Rover ran to the near-fire point for the third time, it successfully implemented the third near-fire brake and successfully entered the parking orbit.
The probe has been on the berthing track for approximately 2.5 months.
This is a high-definition image of Mars taken by Tianwen-1 released by the National Space Administration.
Issued by Xinhua News Agency (Photo courtesy of China National Space Administration)
These four orbit changes are interlocked and closely related to each other. Each time, they must be precisely controlled to ensure that the detector enters the parking orbit smoothly.
Taking into account other factors, the period of this berthing orbit is selected as two Martian days (49.2 hours). During the operation, only a small amount of orbit maintenance is required to ensure that the probe can carry out the scheduled landing area every two Martian days. Check in detail.
Reporter: Hu Zhe
Editor: Li Xiaohu
Source: China National Space Administration, the Eighth Academy of Aerospace Science and Technology Corporation