Igor Denisov, Deputy General Director of the Foundation for Advanced Studies (FPI), announced the creation of the Sarma sea drone in Russia for the needs of the Northern Sea Route (NSR). The project is being implemented by the Lazurit Central Design Bureau for Marine Equipment located in Nizhny Novgorod - the former SKB-112, which was engaged in the USSR in designing submarines of medium displacement.
“We have opened a laboratory at the enterprise to create a demonstrator of an autonomous underwater uninhabited apparatus, and we are starting to manufacture it. By 2020, the creation of three demonstrators is planned, after which the first sea trials on the Black Sea will take place on the route Sevastopol - Sochi and back, ”RIA Novosti quotes Denisov.
A top manager added that in 2022-2023, Sarma could be tested in the Arctic. The device must overcome the "10 thousand km under the ice", that is, the entire Northern Sea Route, passing through the territory of the Russian Federation. Its main task is seismic prospecting and integrated security assurance of navigation along the NSR.
As the head of the FPI design team Viktor Litvinenko specified, “Sarm” will be equipped with an anaerobic (air independent) power plant, which will be environmentally friendly, inexpensive in production and operation.
“This is a very difficult project. It is necessary to pass such a huge distance without errors, and without ascent, without communication with space satellites or the outside world, relying on our own navigation. This will be quite a serious global breakthrough for our country and the development of the world's oceans as a whole, ”explained Litvinenko.
Mastering the depths
The USSR was one of the pioneers in the field of creating uninhabited underwater vehicles (LLA), the L-1 and L-2 robotic complexes were developed, which could sink to a depth of 2 and 6 km, respectively. Drones were widely used for bottom mapping and search operations.
In the 2000s, the specialists of the Institute for Marine Technology Problems (IPMT) of the Far East Branch of the Russian Academy of Sciences created the Clavesin-1R marine drone weighing 2.5 tons and 5.8 meters long. It can dive to a depth of 6 km and 300 km without recharging the batteries . The drone is equipped with an electromagnetic finder, a digital video camera, an acoustic profilograph, temperature sensors and electrical conductivity of sea water.
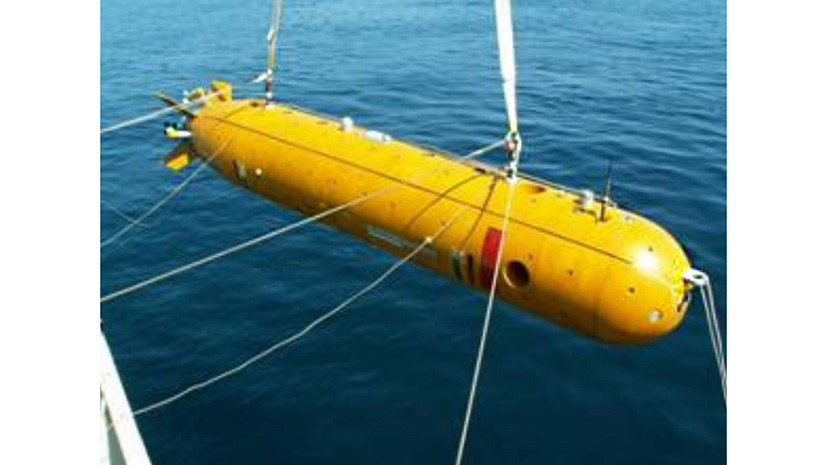

- Autonomous uninhabited underwater vehicle "Harpsichord-1R"
- © Institute of Problems of Marine Technologies of the Far Eastern Branch of the Russian Academy of Sciences
The disadvantages of this NLA include low speed (2.9 knots, or 5.3 km / h), insufficient autonomy and clarity of the “picture”. In 2009, at the request of the Ministry of Defense of the TsBB Rubin (St. Petersburg), the Far Eastern scientists began work on improving the drone, which later received the code 2P52 (“Harpsichord-2R-PM”).
Tests of the device began in 2016 and are currently ongoing. In May 2018, the drone was launched at the test site in Feodosia from an experimental vessel of the project 20360OS “Victor Cherokov” developed by the Nizhny Novgorod design bureau Vympel.
The weight of the “Harpsichord-2R-PM” is 3.7–4 tons, the length is 6.5–7 m, the diameter is 1 m, the depth of the dive is up to 6 km. The device is equipped with electromagnetic sensors, sonars and digital cameras. It is assumed that the new drone will be included in the armament of nuclear submarines of the project 949AM and the special purpose submarine of the project 09787 "Moscow region".
Currently Rubin Central Design Bureau is working on the creation of an unmanned submarine Surrogat equipped with a lithium-ion rechargeable battery. The length of the device is 17 m, the displacement is 40 tons, the depth of immersion is 600 m. The drone can reach speeds of up to 24 knots (44 km / h). The device is supposed to be used mainly for naval exercises.
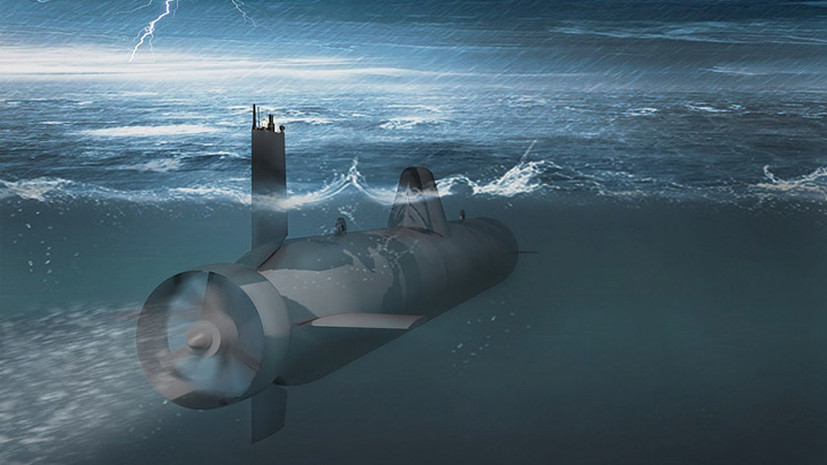
- The image of an unmanned submarine "Surrogate"
- © CDB MT "Rubin"
August 21 at the international forum "Army-2018" the state corporation "Rostec" presented the world's first underwater drone, integrated with a gun, developed by TsNIIochtomash (Klimovsk). The unique APN is designed to protect against saboteurs naval facilities and ships standing on the roadstead.
“The carrier has passed the sea trials, work is under way on integration with weapons, full-fledged trials will begin closer to winter. This is an original development, with small arms, not yet precisely integrated by anyone. In addition, almost no one in the world has an underwater rifle automatic weapon, ”said Rostec.
In the autumn of 2019, FPI is planning to test the Vityaz underwater drone. The device will be immersed at the bottom of the Mariana Trench (depth - 11 km), from where scientists plan to conduct a live broadcast on the Internet. The purpose of the experiment is to map the bottom and collect hydrological data.
“We are committed to ensuring that the picture is transmitted online. It is assumed that the "Vityaz" will consist of two devices: the base station is lowered in the form of a drop, and the device operates around it. Information will be transmitted through the base station, which will be received by the second unit, located within a radius of 150 km, ”Viktor Litvinenko told RIA Novosti.
Large-scale Arctic research
In a conversation with RT, the director of the Museum of the Arctic and Antarctic, Candidate of Physical and Mathematical Sciences Viktor Boyarsky said that the emergence of "Sarma" will be an important stage in the development of the PPA. The capabilities of the current underwater vehicles do not allow effectively performing the functions of ensuring the safety of the Northern Sea Route and the exploration of the Arctic.
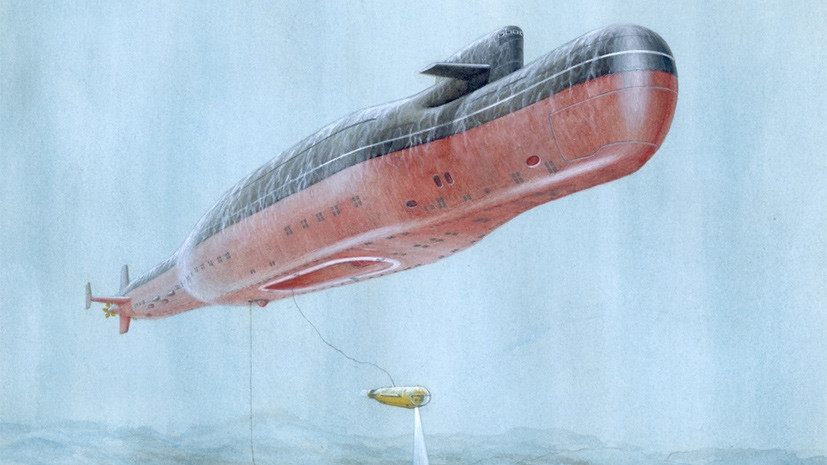
- Image of a submarine cable vessel capable of laying and repairing communication lines
- © CDB MT "Rubin"
“Judging by the stated characteristics and the presence of an anaerobic installation, it will be a fairly large device that performs strategic tasks. He has impressive autonomy. This is an extremely important indicator, since refueling a ship or a submarine with fuel in arctic conditions is an almost impossible task, ”explained Boyarsky.
According to the polar explorer, the nuclear engine is the most optimal for the northern latitudes. The refusal of the specialists of the Central Design Bureau "Lazurit" to use it indicates serious progress in improving anaerobic plants that convert diesel fuel into electricity, says Boyarsky. Now the air-independent engine is used on some foreign submarines, allowing them to be under water for 20 to 45 days.
Also, as suggested by the expert, Russian scientists could improve the way of maintaining communication between the ship and the PPA. According to him, sea drones are most often controlled via cable, which limits their cruising range and maneuverability. If the device is located under the ice, then the signal transmission is possible through the hydroacoustic channel.
The expert believes that the offspring of the Lazurit Central Design Bureau will make it possible to conduct large-scale studies of the Arctic shelf, and in the future it can be reequipped for installation and repair robots of communication cables under the ice.
“Of course, scientists will have to solve many complex problems. Work in the Arctic is not easy, especially in conditions of ice movement. Underwater vehicles sometimes do not even have the ability to surface. However, if Sarma turns out to be a truly effective complex, the development of the NSR and the Polar region will reach a new level, ”concluded Boyarsky.
