What is Gathoum? And how does it happen? What are its causes? And what does a person feel during it? And what is its treatment? The answers are in this report.
What is Gathoum?
Sleep paralysis is a condition in which a person develops a temporary immobility that occurs immediately after falling asleep or waking up. The person remains conscious during a crouching episode, which often involves annoying hallucinations and a choking sensation, according to the Sleep Foundation.
Episodes of sleep paralysis include elements of sleep and wakefulness, which explains why they cause bothersome symptoms.
Gathoum and Jinn
For centuries, people have believed that the jathum is a demonic possession or jinn that a person wears, a belief that has appeared in many civilizations. Valgathoum was the subject of a painting painted by the Anglo-Swiss artist Henry Fusili, and won international fame for centuries, since he painted it in 1781 and presented it to the public in 1782, this painting won unprecedented fame, so that Fuselli painted 3 other paintings revolving around the same idea.
The painting shows a woman who is asleep with her hand drooping, and above her chest is an ugly mythical creature "crouching", which is known in folk legends as the cause of nightmares and paralyzes the movement of the sleeper and cannot move.
However, all these beliefs are false, as the gathoum is a physiological condition that has a scientific explanation, and it is not touched by the devil or worn by the jinn. It is worth noting that the scholar Sheikh Yusuf al-Qaradawi has denied in an interview with Al-Jazeera the subject of wearing jinn with humans.
Symptoms of Gathoum
Sleep paralysis is a condition identified by a brief loss of muscle control, known as Atonia, that occurs immediately after falling asleep or waking up. In addition to asthenia, people often experience hallucinations during episodes of sleep paralysis.
Sleep paralysis is classified as a type of parasomnia, which are abnormal behaviors during sleep. Because it is associated with the REM phase of the sleep cycle, sleep paralysis is a symptom of REM parasomnia.
Researchers believe sleep paralysis involves a mixed state of consciousness that mixes wakefulness and REM phase sleep.
What are the types of sleep paralysis?
- Isolated sleep paralysis: It occurs when seizures are not related to the underlying diagnosis of narcolepsy, a neurological disorder that prevents the brain from properly controlling wakefulness and often leads to sleep paralysis.
- Recurrent sleep paralysis: It involves multiple episodes over time.
What does a person feel in sleep paralysis?
The primary symptom of sleep paralysis is asthenia or inability to move the body. This happens shortly after falling asleep or waking up, and during an episode a person feels awake and is aware of a loss of muscle control.
It is estimated that 75% of sleep paralysis episodes involve hallucinations that differ from the usual dreams.
Hallucinations during sleep paralysis are divided into 3 categories:
- Hallucination of an intruder, which involves the perception of the presence of a dangerous person or his presence in the room.
- Chest pressure hallucinations, also called nursery hallucinations, which can induce a feeling of suffocation. These often occur along with the hallucinations of the intruder.
- "Vestibular-motor VM" hallucinations, which can include a feeling of movement (such as flying) or a sensation of exiting the body.
And annoying hallucinations can make sleep paralysis episodes even more annoying. For this reason, about 90% of seizures are associated with fear.
How long does a bout of jathoum last?
An episode can last from a few seconds to about 20 minutes, and the average duration is between 6 and 7 minutes. In most cases, seizures resolve on their own, but sometimes they are interrupted by someone else's touch or voice or by intense effort to move this overcoming of the weakness.
How common is sleep paralysis?
Estimates vary, but researchers believe that about 8 percent of people suffer from sleep paralysis at some point in their lives.
Sleep paralysis can occur at any age, but the first symptoms often appear in childhood, adolescence or adulthood (7 to 25 years old). After starting in the teenage years, seizures may occur more frequently in your twenties and thirties.
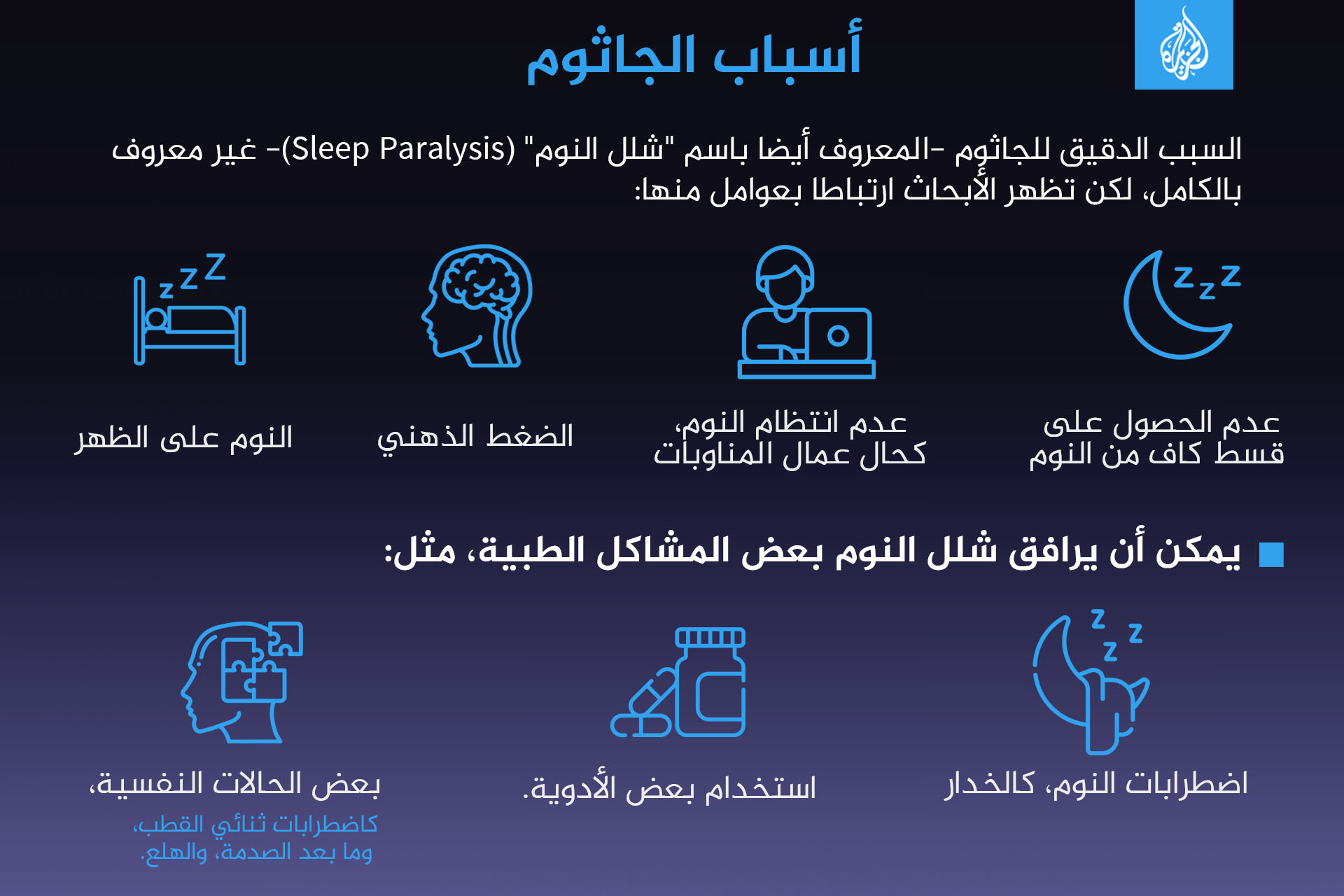
What causes sleep paralysis?
The exact cause of sleep paralysis is unknown. Studies examined the data to see what was associated with an increased risk of sleep paralysis and found mixed results. Researchers believe that multiple factors contribute to sleep paralysis.
Higher rates of sleep paralysis have been reported by people with obstructive sleep apnea (OSA), a condition in which breathing stops during sleep. Sleep paralysis was also found to be more common in people with nocturnal leg cramps.
According to the U.S. National Health Library's Medlineplus database, the exact cause of sleep paralysis isn't fully known, but research shows it is linked to factors such as:
- Not getting enough sleep.
- Having an irregular sleep schedule, as with shift workers.
- Mental stress.
- Sleep on your back.
Some medical problems can be associated with sleep paralysis:
- Sleep disorders, such as narcolepsy.
- Some psychiatric conditions such as bipolar disorder, post-traumatic stress disorder and panic disorder.
- The use of certain medications.
For her part, Assistant Professor Fosun Domaç, a faculty member at the Turkish University of Health Sciences, said that stress and lack of sleep quality are among the most prominent causes of sleep paralysis, in statements to Anatolia.
Is sleep paralysis a serious problem?
For most people, sleep paralysis is not a serious problem, it is classified as a benign condition and usually does not occur frequently enough to cause major health problems.
However, an estimated 10% of people experience frequent or disturbing episodes that make sleep paralysis particularly annoying. As a result, they may develop negative thoughts about going to bed, reducing bedtime or feeling anxious about bedtime, making it more difficult to fall asleep. Sleep deprivation can lead to excessive sleepiness and many other consequences for a person's overall health.
What is the treatment for sleep paralysis?
Dumach said that sleep paralysis, which is not accompanied by any other conditions or diseases, does not require medical treatment, and can be avoided by regulating sleep times, avoiding stress and lack of sleep, and practicing activities that help relax before bed.
The first step in treating sleep paralysis is to talk to your doctor to identify and address underlying problems that may be contributing to the frequency or severity of seizures. For example, this may include treatment for narcolepsy or steps to better control sleep apnea.
Because of the link between sleep paralysis and general sleep problems, improving sleep quality is important.
Tips for healthy sleep that can help improve it include:
- Follow the same sleep-wake schedule every day, including weekends.
- Maintaining a specific bedtime routine helps you feel rested and relaxed.
- Equip your bed with a comfortable mattress and pillow.
- Reduce light and noise.
- Limit caffeine consumption, especially in the evening.
- Keep electronic devices, including mobile phones, away for at least half an hour before bed.