On the second day of April, the world celebrates World Autism Awareness Day, what are its symptoms? What is the incidence rate? What causes it? And what is the treatment?
World Autism Awareness Day
In 2007, the United Nations General Assembly unanimously declared 139 April World Autism Awareness Day (resolution 62/<>), to highlight the need to improve the living conditions of people with autism so that they can live full and meaningful lives, as an integral part of society, according to the United Nations website.
For the 2023 observance, the United Nations has the theme "Transformation: Towards an inclusive world of neurodiversity for all".
What is autism?
Autism spectrum disorders (ASD) is a lifelong neurological condition that appears in early childhood, regardless of gender, race, or socioeconomic status.
It is also a group of diverse disorders characterized by some difficulties in social interaction and communication, and has other features in the form of patterns of activities and behaviors such as difficulty moving from one activity to another, absorbing in details, and unusual reactions to sensations, according to the World Health Organization.
Symptoms of autism
Symptoms of autism associated with communication skills and social interaction
- Avoid or maintain eye contact, according to the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
- Infant unresponsiveness when called by name at 9 months of age.
- No facial expressions such as happiness, sadness, anger and surprise appear on a 9-month-old baby.
- He does not play simple games by the age of 12 months.
- Uses few or no gestures by the age of 12 months (for example, no goodbye wave).
- Does not share interests with others by the age of 15 months.
- He doesn't point out to tell parents about something that interests him by 18 months.
- It is not noticed when others are hurt or upset by the age of 24 months.
- Children do not notice and do not join them in play by 36 months.
- Don't pretend to be another character, such as pretending to be a teacher or superhero, while playing at 48 months.
- He doesn't act on anything to interest parents — for example, singing — by 60 months of age.
Autism symptoms associated with restricted or repetitive behaviors or interests
Children with autism have behaviors or interests that may seem unusual, such as:
- The order of toys or other objects and discomfort when changing their order.
- He repeats the same words or phrases frequently.
- He plays with toys the same way every time.
- Focuses on parts of objects (for example, wheels in a toy car).
- Disturbed by minor changes.
- Fluttering hands or spinning in circles.
- It shows unusual reactions to the way things look, smell, taste, look or feel.
Symptoms of autism associated with language and mood
- Delayed development of language skills.
- Delayed development of motor skills.
- Delayed cognitive or educational skills.
- Impulsive behavior.
- Epilepsy disorder or seizures.
- Unusual eating and sleeping habits.
- Digestive problems (such as constipation).
- Unusual mood or emotional reactions.
- Anxiety or stress.
- There is no fear or there is more fear than would be expected in such a case.
It is important to note that children with autism may not have all or any of the behaviors listed as examples here.
Causes of autism
There is no single cause of autism spectrum disorder. There are many different factors that have been identified, which may make a child more susceptible to autism, including environmental, biological and genetic factors.
Although we know little about the specific causes, available evidence suggests that the following may put children at greater risk of developing autism spectrum disorder:
- The presence of a sibling with autism spectrum disorder.
- Certain genetic or chromosomal conditions, such as fragile X syndrome or tuberous sclerosis.
- Suffering from complications at birth.
- The child must be born to older parents.
Fragile X syndrome is a genetic disorder in which changes occur in a gene called Fragile X Messenger Ribonucleoprotein 1 (FMR1). This gene usually makes a protein necessary for brain development called FMRP, and people with fragile X syndrome don't make this protein.
Tuberous sclerosis is an uncommon genetic disorder that causes tumors to grow in many parts of the body. These tumors aren't cancerous, according to the Mayo Clinic.
Vaccination does not cause autism, which is a common fallacy, and vaccinations or triple vaccination have no connection to autism spectrum disorders.
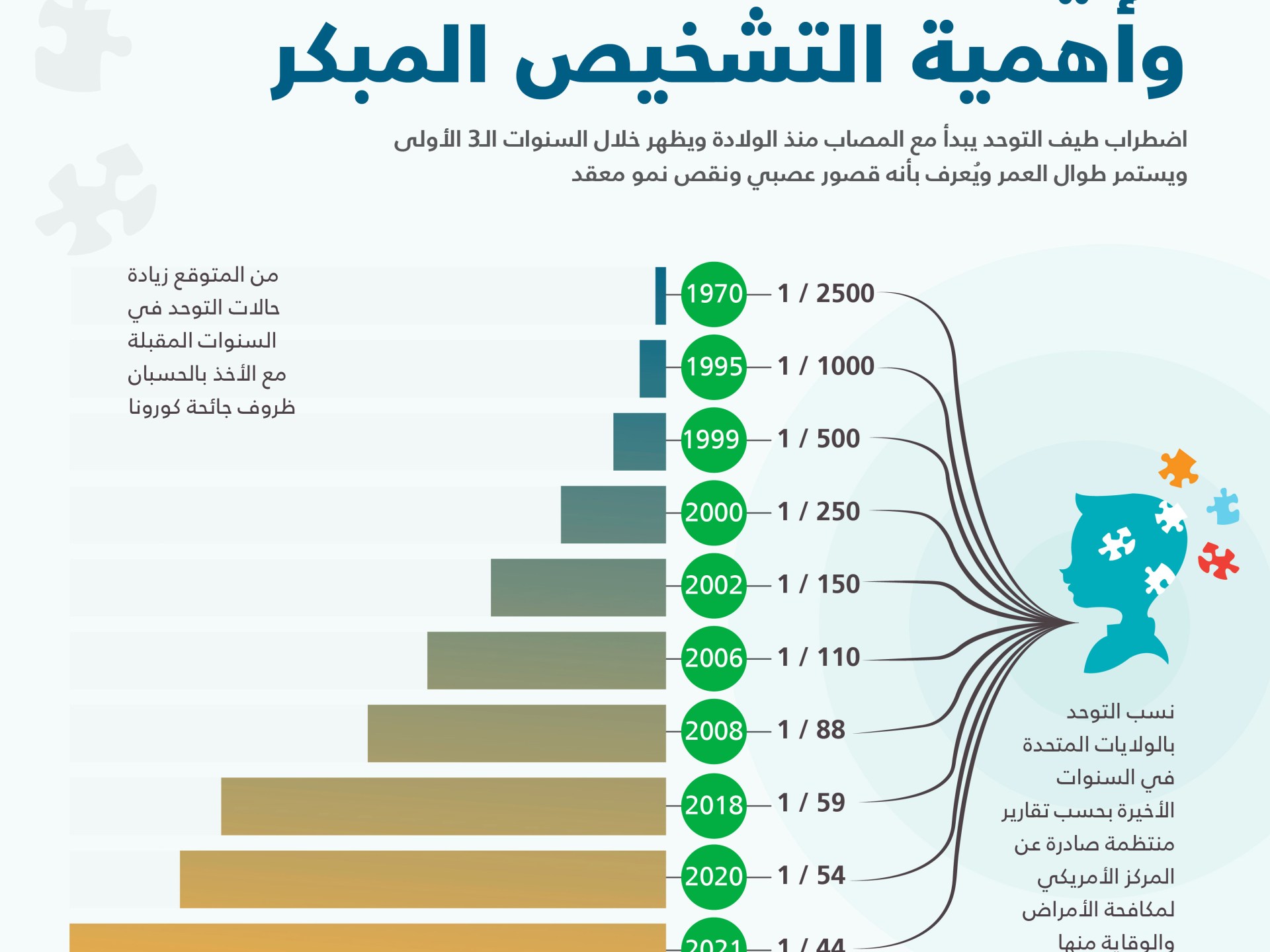
Incidence of autism
The World Health Organization estimates that one in 100 children in the world has autism.
Types of autism
Here are the types of autism arranged from less severe to more severe symptoms
Asperger's syndrome
It is a mild type of autism spectrum disorder. A person with Asperger's syndrome may be very intelligent and able to cope in their daily life, and may be able to focus on topics that interest them and discuss them non-stop, but they may face some social difficulties.
Pervasive developmental disorder, not otherwise specified (PDD-NOS)
This type includes most children who have autism more severe than Asperger's syndrome, but not as severe as autism disorder.
Autistic disorder
This type includes the same types of symptoms, but at a more severe level.
Childhood disintegrative disorder
This type is the rarest and most severe part of autism spectrum disorders, and affected children usually develop normally and then quickly lose many social, language and mental skills, especially between the ages of 2 and 4.
Diagnosis of autism
Autism features can be detected in early childhood according to the symptoms mentioned earlier, but it is often not diagnosed until long after this stage, according to the World Health Organization.
Autism treatment
There is no cure for autism, and current treatments for autism spectrum disorder seek to reduce symptoms that affect daily functioning and quality of life.
Behavioral therapy
Behavioral approaches focus on changing behaviors by understanding what happens before and after behavior. Behavioral therapy for people with autism is called applied behavior analysis (ABA).
Developmental Curricula
Developmental approaches focus on improving specific skills, such as language or physical skills, or a wide range of interrelated developmental abilities. Developmental approaches are often combined with behavioral approaches.
The most common developmental treatment for people with autism is speech and language therapy. Speech and language therapy helps to improve a person's understanding and use of speech and language. Some people with autism spectrum disorder communicate orally. Others may communicate through the use of gestures, gestures, images, or an electronic communication device.
Educational Curricula
Instructional therapies are offered in a classroom setting, providing teachers with ways to adjust the classroom order and improve academic and other outcomes. For example, the daily routine can be written or drawn for the student.
Social Relations Curricula
Social relationship therapies focus on improving social skills and building emotional bonds.
Medications
There are no medications that treat the underlying symptoms of autism spectrum disorder. Some medications treat comorbidities that can help people with autism spectrum disorder do their job better.
For example, medications may help improve the ability to concentrate or prevent self-injurious behavior, such as hitting the head or biting your hand. Medications can also help manage associated psychiatric conditions, such as anxiety or depression, as well as medical conditions such as seizures, sleep problems, stomach problems or other digestive problems.
Psychotherapy
Psychological approaches can help people with autism cope with anxiety, depression, and other mental health problems. Cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) is a psychological technique that focuses on learning the connections between thoughts, feelings, and behaviors. During cognitive behavioral therapy, the therapist and individual work together to set goals and then change the way the person thinks about the situation to change the way they react to the situation.