Rome discovers the names of its baby gangs, from
Garbatella
(the "17") to the
Eur, to North Rome
(the "18").
They have their own slang their hangouts and it all happens via chat.
They are teenagers who strike in
packs
, they spread the videos of the victims and also those that the peers have granted to the boyfriends in a moment of intimacy.
A phenomenon in great expansion, so much so that more and more often the media deal with them.
Some data: in Italy from January to April 2022 1909 articles were published containing references to “
youth gangs” or “baby gangs”
in national and local newspapers or press agencies.
This number alone exceeds the total number of similar articles published across 2021 (1249) and is more than twice the number of articles in 2020 (741).
Despite the relevance of this problem, the outlines of the concept of youth gang often remain uncertain and tend to include
different
behaviors or types of groups, even very different from each other, but at the moment there is a lack of data that allows for systematic monitoring of this phenomenon. and its characteristics.
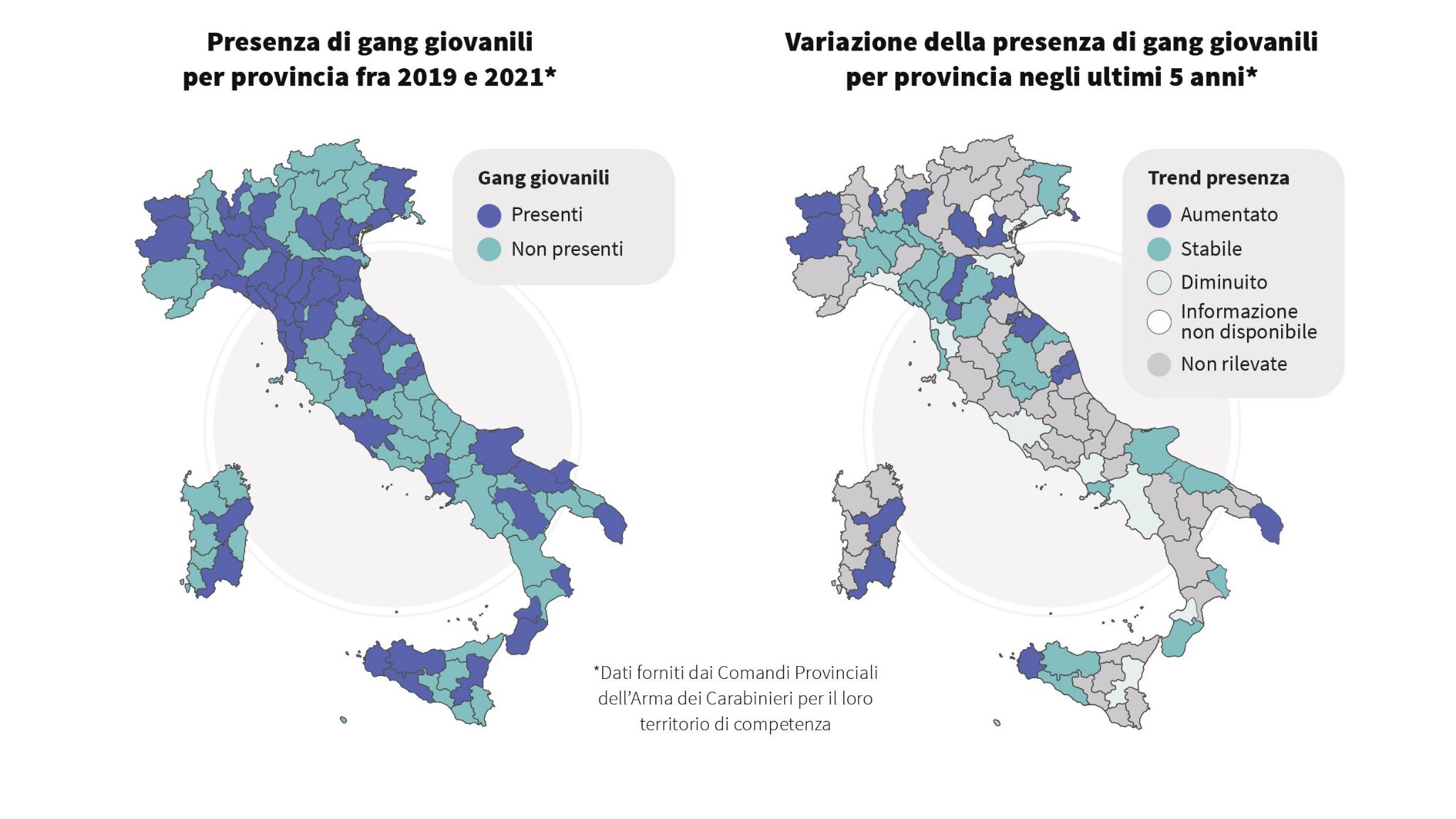
A first representative photograph of the phenomenon, also for geographical areas and typologies, was made by
Transcrime
, the inter-university research center on transnational crime of the Catholic University of the Sacred Heart, Alma Mater Studiorum University of Bologna and University of Perugia, in collaboration with the Criminal Analysis Service of the Department of Public Security of the Ministry of the Interior and the Department for Juvenile and Community Justice of the Ministry of Justice.
Ministry of the Interior
Youth gangs in central Italy
The title is
"The youth gangs in Italy"
and which put together information collected through two different questionnaires, one of which administered to the Provincial Commands of the Carabinieri and the Police Headquarters and the other to the Social Service Offices for Minors ( USSM).
This data was further integrated through the collection and analysis of news that appeared in national and local newspapers or news agencies.
In particular, the report found that youth gangs:
- they are active in most of the Italian regions (with a slight prevalence of the
Center-North compared to the South of the country
).
Furthermore, according to half of the Social Service Offices for Minors and 46% of the Police Headquarters and Provincial Carabinieri Headquarters in the last five years have increased in their area of competence.
- they are mainly composed of less than
10 individuals,
mostly males and aged between 15 and 17 years.
In most cases the gang members are Italian, while groups formed mostly by foreigners or without a prevalent nationality are less frequent.
-The crimes most often attributed to them are violent crimes, such as fights, beatings and injuries,
bullying
, disturbance of the peace and vandalism.
Less frequent and usually committed by more structured groups are drug trafficking or appropriative crimes such as theft and robbery.
The most frequent victims of these groups are other young people between the ages of 14 and 18.
There are four main types of gangs present in Italy with different characteristics and a different distribution on the territory:
-groups
without
a defined structure, mainly engaged in occasional violent activities (eg fights, beatings and injuries) or deviant: present in all the macro-areas of the country, they are the type that is most noted and most consistent in number.
These groups are characterized by weak links, a more fluid nature, the absence of a clear hierarchy or defined organization, and often also of specific criminal purposes.
- groups that are inspired by or have
links with Italian criminal organizations
: present especially in the South of the country in urban contexts where there is historically a mafia presence.
They are made up almost entirely of Italians with a high involvement of minors.
These groups are often linked to the desire to increase their criminal status with the hope of becoming part of the aforementioned criminal organizations.
-groups inspired by criminal organizations or
foreign gangs
: mainly present in urban areas of the North and Center of the country and mainly composed of first or second generation foreigners.
Among the criminal activities most often associated with this type of gang there are fights, beatings and injuries, vandalism and disturbance of the public peace.
- groups with a
defined structure
but without references to other organizations and dedicated to specific criminal activities: present in all the macro-areas of the country and composed mainly of Italians.
They often carry out appropriative crimes, such as thefts or robberies, but also violent crimes.
These gangs are usually not endowed with particular symbols nor do they have an interest in advertising their actions.
Some of the factors that influence children and push them to join these groups are: problematic relationships with
families,
peers or the school system;
relational difficulties or inclusion in the social fabric;
and a context of social or economic hardship.
Many of these factors were further exacerbated during the pandemic period.
In fact, many studies have shown how the recent
Covid-19
pandemic has had a strong impact on the daily lives of children, causing a worsening of the objective and subjective conditions of personal well-being.
Another factor is the use of social networks as a tool to strengthen group identities and generate processes of emulation or self-fulfillment.
Transcrime Director, Professor
Ernesto Savona
, commented: “Understanding the problems is the basis for developing truly effective intervention strategies.
To do this, the collection and analysis of data in a systematic way is essential.
This exploratory relationship is therefore only a first step towards a synergistic commitment between the world of research and public authorities to counter a complex and rapidly evolving problem such as that of youth gangs ”.
Ministry of the Interior
Youth gang in Lombardy
Finally, the report reports several
concrete examples
of youth gangs detected in the area and the current measures to combat the phenomenon are briefly discussed together with some intervention proposals for a better social reintegration of young people.
There are many reasons for the creation of these groups, young people can in fact seek in these gangs a response to a
state of social isolation,
dissatisfaction with their condition or inability to relate to their peers.
As far as the composition of these gangs is concerned, from the data collected it emerged that in almost half of the cases they are composed mainly of
Italians,
and less than one in three is mainly composed of foreigners.
Members are generally between the ages of
15 and 17,
although in almost a quarter of cases the prevailing age is between 18 and 24 years.
Most of these groups are made up of fewer than 10 individuals and in less than half of the cases the members are in socio-economic distress.
Lacking a defined organization, these youth gangs are mainly identifiable starting: from their activity on social networks, from the repetitiveness of the crimes committed and from the socio-personal characteristics of the members.
Groups with no defined structure engaged in violent or deviant activities
It is the
model
most present on the national territory and numerically more consistent.
These groups are characterized by weak bonds, a more fluid nature, have no defined structure.
they are engaged in violent or deviant activities.
The crimes most frequently committed by this type of gang are occasional violent or deviant activities.
Ministry of the Interior
Youth gangs in Italy
Groups that are inspired by or have links with Italian criminal organizations
The
second type
includes groups that are inspired by or have direct connections with traditional Italian criminal organizations.
Several Provincial Commands of the Carabinieri and Police Headquarters have declared that they have found the presence of links between youth gangs and other criminal organizations.
These ties are often family ties or linked to collaboration in criminal activities.
These youth gangs have been found especially in
the south of the country
in urban contexts where there is historically a mafia presence.
In particular, in the provinces of Naples, Salerno, Reggio Calabria, Crotone, Vibo Valentia and Caltanissetta.
However, sporadic cases have also been highlighted in the provinces of Milan, Modena, Fermo, Florence and Vercelli
Ministry of the Interior
Youth gangs in Italy
The Deputy Director General of Public Security, Prefect Vittorio Rizzi, declared: “The police forces constitute a privileged observatory on the deviations that afflict the world of young people.
The search for identity, the importance of belonging to a group, the sense of omnipotence typical of the young age, the life that develops above all on social networks, the restrictions caused by lockdowns and pandemics are just some of the causes of a phenomenon that it is improperly defined as the baby gang or the malamovida.
Clashes between more or less organized groups of young people, acts of violence and hooliganism that often have other bullied minors as victims, who find it hard to report.
Our task is to intercept the phenomena of discomfort in the bud, intervene to avoid an escalation of violence and, above all,
Ministry of Interior
Youth gangs in Italy