Intellectual property protection delineates construction drawings, and comprehensively establishes a punitive damages system
The specific plan for the protection and use of intellectual property rights in China has been released.
On the 28th, the State Council announced the "Fourteenth Five-Year Plan for the Protection and Utilization of Intellectual Property Rights" (hereinafter referred to as the "Plan") issued a few days ago, which has comprehensive arrangements for the work of intellectual property rights in the next five years.
The "Plan" pointed out that by adhering to quality priority, strengthening protection, open cooperation, and system coordination, by 2025, the phased goals and tasks of building a strong intellectual property country will be completed on schedule, the governance capacity and level of the intellectual property field will be significantly improved, and the intellectual property business will achieve high quality Development, effectively supporting innovation-driven development and the establishment of a high-standard market system, effectively promoting high-quality economic and social development.
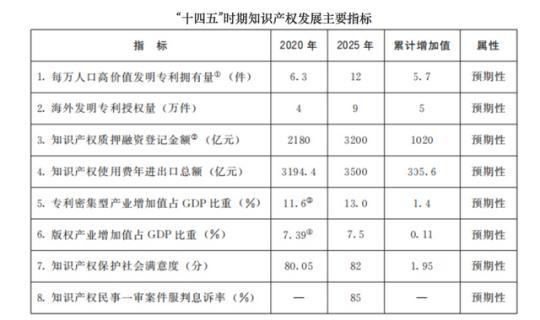
The "Plan" proposes four main goals for intellectual property protection to a new level, new results in the use of intellectual property, new levels of intellectual property services, and new breakthroughs in international intellectual property cooperation. The establishment of "the number of high-value invention patents per 10,000 population" And other eight main expected indicators.
It also deployed key tasks around five major areas, and set up 15 special projects including the business secret protection project.
You Minjian, an arbitrator and mediator of the World Intellectual Property Organization Arbitration and Mediation Center, told China Business News that, compared with the “Outline for Building a Powerful Intellectual Property Country (2021-2035)” which is positioned as a mid-to-long term, the “Plan” is geared towards intellectual property work. The implementation of each unit and department issued more targeted tasks to ensure that all tasks are implemented in place.
The specific measures, coupled with more than a dozen columns, not only ensure the comprehensive implementation of intellectual property work, but also highlight the key tasks during the "14th Five-Year Plan" period.
Yang Yong, a researcher at the Institute of Intellectual Property Law and Policy of East China University of Political Science and Law, told China Business News that the "Plan" is clearer and clearer in terms of operation, implementation and work objectives. It has taken the protection of intellectual property rights to a new level, and clearly requires the connection mechanism of intellectual property protection. More complete, effective implementation of the punitive compensation system for infringement of intellectual property rights, effective containment of the frequent occurrence of infringements, and more high-quality intellectual property rights in key core technology areas.
Strengthen administrative protection and implement punitive damages
In terms of comprehensively strengthening the protection of intellectual property rights and stimulating the innovation vitality of the whole society, the "Plan" includes several aspects including improving the intellectual property legal and policy system, strengthening the judicial protection of intellectual property, strengthening the administrative protection of intellectual property, strengthening the coordinated protection of intellectual property, and strengthening the source of intellectual property protection. Specific measures have been proposed.
Among them, in terms of improving the administrative protection mechanism of intellectual property rights, it is proposed to strengthen the central government’s power in intellectual property protection in terms of macro-management, regional coordination, and coordination of foreign-related matters; establish an administrative protection technical investigator system; improve the administrative adjudication system for intellectual property infringement disputes; Regional and inter-departmental intellectual property administrative protection coordination mechanisms, etc.
"This "Plan" has new thinking on strengthening administrative protection." Yang Yong said, for example, proposing to strengthen the construction of the intellectual property administrative enforcement guidance system, establish the administrative protection technical investigator system, and improve the cross-regional and cross-departmental intellectual property administrative protection cooperation mechanism.
It also proposed to strengthen the staffing and capacity building of the administrative enforcement of intellectual property rights and administrative adjudication teams.
In his view, many hot issues of intellectual property rights need to be resolved by administrative protection, but the existing administrative team mechanisms and capabilities are still inadequate.
Therefore, it is expected that relevant and more specific administrative protection regulations will improve protection efficiency.
"We also need to optimize the systems and mechanisms for the administrative protection of intellectual property rights, and strengthen the talent construction of the intellectual property team to ensure the professionalization and efficiency of the team." Yang Yong said.
In addition to administrative protection, the "Plan" proposes to comprehensively establish and implement a punitive compensation system for infringement of intellectual property rights to increase damages.
Since 2018, the legal revision and policy formulation of the intellectual property punitive damages system have been accelerated.
Intellectual property sector laws such as the Anti-Unfair Competition Law revised in 2019, the Patent Law and the Copyright Law revised in 2020 have all added punitive damages clauses.
The "Civil Code" promulgated in 2020 provides for the system of punitive damages for intellectual property rights, marking the realization of "full coverage" of punitive damages in the field of intellectual property rights.
In the decision to amend the "Trademark Law" announced on April 23, 2019, it is clear that the amount of compensation for malicious infringement of trademark exclusive rights will be increased from less than three times before the revision to less than five times, and the statutory compensation limit is increased from 3 million Yuan increased to 5 million yuan, and the amount of punitive damages reached a relatively high level in the world.
On this basis, the 2019 "Opinions on Strengthening the Protection of Intellectual Property Rights" further proposes to speed up the revision and improvement of the "Patent Law", "Trademark Law", and "Copyright Law", greatly increase the upper limit of legal compensation for infringement, and increase The intensity of damages.
On March 3, 2021, the Supreme People's Court issued the "Interpretation of the Supreme People's Court on the Application of Punitive Compensation in the Trial of Civil Cases of Infringement of Intellectual Property Rights" (hereinafter referred to as the "Interpretation"), which will take effect on that day.
The "Interpretation" made specific provisions on the scope of application of punitive damages in civil intellectual property cases, the determination of intentional and serious circumstances, and the determination of calculation bases and multiples.
The aim is to guide courts at all levels to accurately apply punitive damages and punish serious violations of intellectual property rights through clear judgment standards.
Liu Chunquan, a partner of Duan and Duan Law Firm, believes that China's intellectual property laws and policies have been relatively complete, and what is more important is how to better implement them in practice.
"When specific laws fall into the case, it is not easy to convince people that the company has indeed suffered a lot of losses."
Open the way for emerging industries and key core technologies
In innovation activities, intellectual property plays a key supporting role.
High-quality development places urgent demands on higher-level creation and higher-efficiency use of intellectual property rights.
The first of the basic principles of the "Plan" is to insist on quality first and accelerate the transformation of intellectual property work from pursuing quantity to improving quality.
The "Plan" also puts forward several indicators. For example, by 2025, the added value of patent-intensive industries will account for 13% of GDP, the added value of copyright industry will account for 7.5% of GDP, and the total annual import and export of intellectual property royalties will reach 350 billion. Yuan, the number of high-value invention patents per 10,000 people has reached 12.
However, in Yang Yong's view, compared with European and American countries, the quality of China's intellectual property rights is still inadequate.
To build a country with a strong intellectual property rights, it is necessary not only to have quantitative advantages, but also to have advantages in some key areas.
Shen Changyu, director of the State Intellectual Property Office, also mentioned in a signed article in the "People's Daily" on the 23rd that building a strong country with intellectual property rights is an urgent need to promote high-quality development.
Vigorously develop new technologies, new business forms, and new models, develop an innovative economy supported by patents, a brand economy supported by trademarks, a characteristic economy supported by geographical indications of origin, and a cultural industry supported by copyright. The turnaround of the seed industry itself is the meaning of high-quality development, and it is the key to shaping China's new advantages in future development and achieving high-quality development.
The "Plan" proposes to improve intellectual property protection policies.
Improve the intellectual property protection system in new fields and new business forms such as big data, artificial intelligence, and genetic technology.
Research and construct data intellectual property protection rules.
Improve the intellectual property policy for safeguarding national security.
To study and formulate intellectual property protection rules for key core technologies related to national security.
"This "Plan" is more to play an escort role for the protection and development of intellectual property rights in emerging industries, and to provide a good atmosphere for intellectual property protection for these new technologies." Yang Yong said.
In You Minjian's view, among the specific measures involved in the "Plan", the first "improvement of the intellectual property legal policy system" mentioned "improvement of the intellectual property legal system linked to the construction of national defense."
At the same time, in the specific measures, there is also a section of "Improving the Intellectual Property Policy for National Security", including the protection of intellectual property rights of key core technologies related to national security, and the legal management of the external transfer of intellectual property rights related to national security.
"These contents related to national security are not included in the 13th Five-Year Plan for the protection and use of intellectual property rights. The reason is that this "plan" also mentioned that China's economy has shifted from a stage of rapid growth to a stage of high-quality development. Intellectual property is now a strategic resource for national development and a core element of international competitiveness. As a competitive weapon, intellectual property can maintain the foundation of independent innovation in the new round of scientific and technological revolution." You Minjian said.
Liu Chunquan told reporters that the "Planning" also mentioned trade secret protection projects and data intellectual property protection projects.
"Through legal policies and comprehensive measures to guide the government to strengthen market protection, this is more scientific than modifying a legal rule alone, and will have a practical effect on innovation." He reminded that major innovations are not achieved overnight, and legislative rules must also be prevented. High encourages the emergence of "intellectual property cockroaches", and frequently initiates lawsuits to demand excessive fees from enterprises that truly do business, which hinders normal business competition.
(Author: Jin Ye Zi)