What causes appendicitis?
And what are its symptoms?
What cases can be confused with appendicitis?
What are the signs of appendicitis bursting?
And how to deal with suspicion of inflammation?
We emphasize at the outset that the information provided here is indicative, and not a substitute for consulting a doctor.
If you have abdominal pain or suspect you may have appendicitis,
call 911 immediately
.
Appendicitis is a condition in which the appendix, which is a small, thin pouch about 5 to 10 cm long connected to the large intestine where stool is formed, becomes inflamed, according to the UK's National Health Service.
The appendix is located in the lower right part of the abdomen.
What causes appendicitis?
The causes of appendicitis are not clear, and in many cases there may be something blocking the entrance to the appendix causing it to become inflamed, such as a small piece of stool, worms or a foreign object.
If the blockage causes inflammation and swelling, it can increase pressure within the appendix, which may then burst.
Because the causes of appendicitis aren't fully understood, there's no foolproof way to prevent it.
You can get appendicitis at any age, but it usually affects young people between the ages of 10 and 20, according to the UK's National Health Service.
What are the symptoms of appendicitis?
There are several symptoms of appendicitis, and they are as follows:
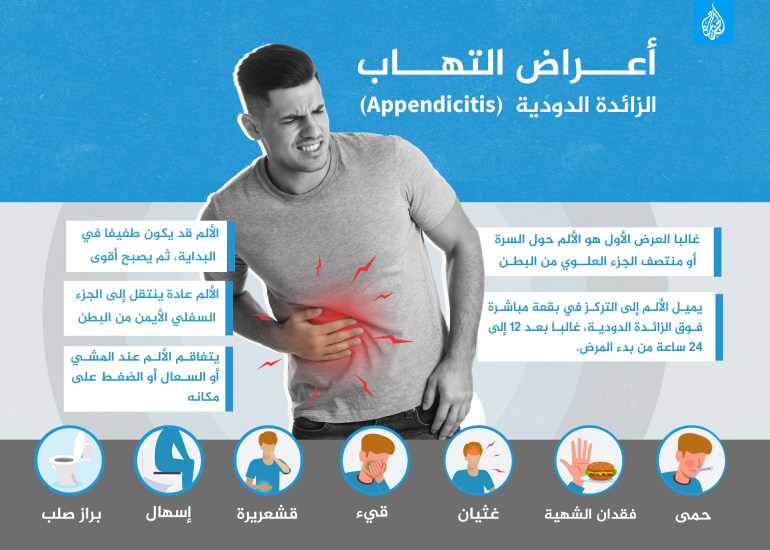
Often, the first symptom is pain around the navel or the middle of the upper abdomen.
The pain may be slight at first, then become stronger.
The pain usually travels to the lower right part of the abdomen.
The pain tends to travel to the lower right part of your abdomen.
The pain tends to be concentrated in a spot directly above the appendix called the McBurney point.
This often occurs 12 to 24 hours after the onset of illness, according to the US National Library of Health.
The pain worsens when walking, coughing, or applying pressure.
goosebumps
hard stools
Diarrhea
Fever
nausea
vomiting
Anorexia
What conditions can be confused with appendicitis?
Appendicitis can easily be confused with some other conditions, such as:
Inflammation of the stomach and intestines
Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS)
constipation
Bladder infections or urinary tract infections
Crohn's disease
pelvic infection
In women, symptoms of appendicitis may be similar to those of gynecological conditions, such as an ectopic pregnancy, menstrual pain or pelvic inflammatory disease.
What are the signs of appendicitis bursting?
If the pain subsides for some time and then gets worse, this may mean that the appendix has ruptured, which can lead to life-threatening complications.
If you feel this, you should
call 911 immediately
.
A ruptured appendix can cause peritonitis, a serious infection of the inner lining of the abdomen.
The MSD Manual says that rupture of the appendix may lead to the formation of pus (an abscess).
As a result, peritonitis may occur.
In women, the ovaries and fallopian tubes may also become infected, and the resulting scarring can block the fallopian tubes, causing infertility.
A ruptured appendix may also cause germs to pass into the bloodstream, a life-threatening condition called sepsis.
How long does it take for appendicitis symptoms to start and burst if it isn't treated?
According to the MSD Manual, surgery is the main treatment for appendicitis, and delaying surgery until the cause of abdominal pain is known can result in death, as an infected appendix can rupture less than 36 hours after symptoms begin.
How to deal when suspected appendicitis?
Any condition that causes persistent abdominal pain requires urgent medical attention.
Call 911 if you have pain that suddenly gets worse and spreads through your abdomen, or if the pain temporarily improves before it gets worse again.
Most of the time, your surgeon will remove your appendix as soon as you're diagnosed.
It usually takes two weeks for a full recovery after the appendix is removed.
But strenuous activities may need to be avoided for up to 6 weeks after open surgery.