China News Service, July 19. Climate change is one of the top international events today, and various changes brought about by global warming are becoming more and more significant.
The British Broadcasting Corporation (BBC) recently published an article that the United Nations has proposed an upper limit for global warming-the temperature is up to 1.5°C higher than the pre-industrial era. However, scientists believe that to achieve this goal, the premise is that all levels of social life occur rapidly, A long-term, unprecedented change.
Wildfires are raging in Oregon, USA.
The picture shows a large flaming cumulus cloud floating over the fire field.
The global warming trend continues, and non-intervention will have catastrophic consequences
To put it simply, climate change is the greenhouse gas effect that causes the earth's temperature to rise and global warming.
This trend began with industrialization in the middle of the 19th century and continued.
The key issue is that the current temperature rise is accelerating, surpassing any previous period; and the impact of climate warming on all aspects of the earth's ecology is becoming more and more significant.
According to data from the World Meteorological Organization (WMO), the current temperature on the earth is nearly 1°C higher than before industrialization began to spread.
According to this trend, by 2100, the global temperature will be 3 to 5°C higher than the pre-industrial level.
In the past 22 years, there have been 20 years of the highest temperature ever recorded, and 2015 to 2018 were the 4 years with the highest temperature.
It sounds trivial, but the United Nations Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) pointed out that if interventions are not taken, there will be catastrophic consequences: sea level rises, some islands and coastal lowlands will be submerged; sea temperature and acidity rise; Agriculture and animal husbandry will face challenges.
Human activities have caused a significant increase in greenhouse gases, intensifying the
greenhouse effect
Climate warming is related to the greenhouse effect-the sun shines on the surface of the earth, then reflects back to the sky, is absorbed by carbon dioxide (greenhouse gas) in the atmosphere, and then released everywhere.
During this naturally occurring process, the temperature of the atmosphere and the earth's surface near the ground will rise.
If there is no greenhouse effect, the earth will be cold and unsuitable for life.
However, the data shows that human activities have greatly increased the greenhouse gases emitted into the atmosphere, intensifying the greenhouse effect and the warming of the earth.
Therefore, climate change is also called global warming.
Carbon dioxide, methane, nitrous oxide, etc. are all greenhouse gases, but carbon dioxide (CO2) plays a major role in climate change.
From 1959 to 2019, global carbon emissions increased year by year.
The carbon dioxide produced by human activities mainly comes from the burning of fossil fuels.
In addition, clearing land and logging will also increase carbon emissions and exacerbate global warming.
According to the report, it will take hundreds of years to reduce the carbon dioxide content in the atmosphere to the pre-industrial level.
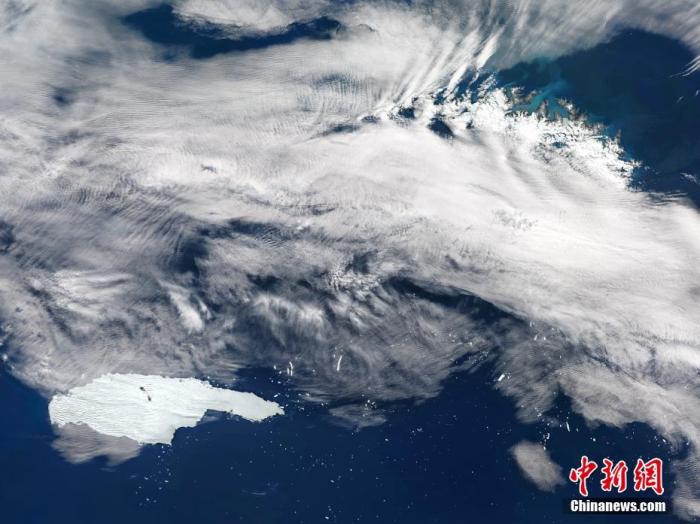
The "world's largest iceberg" code-named A68 near Antarctica has melted and decomposed into many small icebergs.
The picture shows the world's largest iceberg A68a drifting towards South Georgia on December 2, 2020, local time.
Image source: Visual China
Extreme weather, collapse of ice shelves... Nature sounds the alarm
For decades, academia believed that by the end of this century, the Earth’s temperature rise should be controlled at a level 2°C higher than the pre-industrial average to be considered “safe” and to avoid the “worst-case scenario” from happening.
At present, it is recognized that the main cause of sea level rise is accelerated melting of glaciers and ice layers.
The area of the ice sheet between the north and south of the earth is shrinking.
Satellite images show that the area of sea ice in the Arctic is shocking compared to 1979. In particular, the Greenland ice shelf collapsed due to unbearable temperature rise, and the East and West Antarctic ice sheets are shrinking.
A report by the British Parliament’s Environmental Affairs Audit Committee stated that at the current rate of temperature rise, there will be no more sea ice in the Arctic Ocean in summer by 2050.
The impact of climate change is also reflected in the changes in vegetation and terrestrial animals, including early flowering and fruiting, and changes in the activity areas of wild animals.
Ninety-five percent of cities in Africa and Asia face climate risks, and the fastest-expanding cities are most at risk.
These risks include a significant increase in temperature and an increase in extreme weather and natural disasters.
Related to everyone, how to combat climate change?
Effective response to climate change has become an important issue for the international community and governments of all countries, and non-governmental organizations, social groups, and environmental organizations are also working in their respective fields.
However, climate change is closely related to everyone living on the earth.
Everyone’s life will be affected by climate change, and everyone can contribute as much as they can to mitigate the impact of climate change.
The United Nations Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) has given many lifestyle choices that can help combat climate change:
Eat less meat, dairy products, cheese, butter, and eat more local aquatic products, fruits and vegetables to reduce waste;
Take more trains and buses, less planes, and drive electric cars instead of driving if you can walk or ride a bicycle;
Hold more video conferences to reduce business travel;
Use less dryer and more clothesline;
Improve the insulation protection of your own house and reduce heat loss;
Consciously choose low-carbon products when shopping;
In addition, changing the diet is also the most direct way to participate.
"Science" magazine published a research result that showed that the impact of the same food on the environment varies significantly due to the different production processes.
Take beef, for example, if forests are cleared for building a cattle farm, the carbon emissions of beef from this cattle farm are 12 times that of cattle on natural pastures.