What are the side effects associated with the different types of emerging corona virus "Covid-19"?
The answer is here, in this report, in which we compare 8 vaccines for Corona in terms of side effects, with a detailed infographic.
We based this report on a paper entitled "A Close Look at the Covid-19 Vaccines: The Known, the Unknown and the Uncertain", authored by Nadine Hilal, Nada Melhem and Fadi Al-Jardali, and published by the American University of Beirut.
We also consulted data from the US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, the US Food and Drug Administration, news sites like business insiders, and news sites.
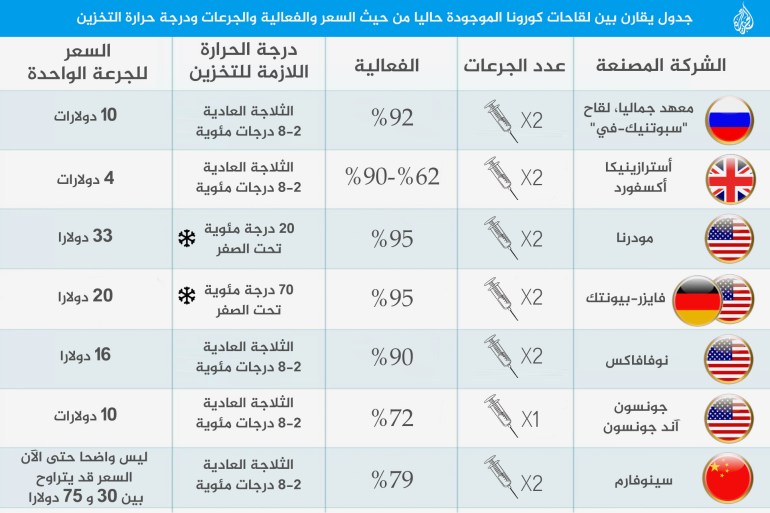
These are the differences between 8 vaccines for Corona in one table:
How do these different vaccines work?
1- "Pfizer-BioNTech"
vaccine: the vaccine consists of a lipid capsule that contains parts of messenger RNA (mRNA), or what is known as messenger RNA, which encodes the "spike" protein for the Corona virus, whose scientific name is " SARS Cove-2 ".
The mRNA is modified slightly so as not to cause too much inflammation.
After injection, the messenger RNA enters the muscle cells and stimulates the production of spike proteins, which the immune system will recognize, and thus learn to defend itself against the "SARS-CoV-2" virus.
2- The
moderna
vaccine
: (like the Pfizer-Biontech vaccine) consists of a lipid capsule that contains fragments of messenger RNA, and contains the code for the SARS-Cove-2 spike protein.
Capsule preparation and mRNA inoculation differ slightly, but their roles are identical.
After the injection, vaccination of mRNA enters the muscle cells, stimulates the production of "spike" proteins and helps our immune system to recognize and fight the virus.
3- Oxford-AstraZeneca vaccine
: It works with the viral vector technology, and in this vaccine, the viral vector, the chimpanzee adenovirus (Adenovirus) has been genetically modified to reduce its reproduction.
The SARS-Cove-2 virus 'spike' protein gene is then inserted into the genome of this viral vector.
Once injected, the virus enters the muscle cells.
It then produces a "spike" protein that allows the immune system to learn to recognize and fight the SARS-Cove-2 virus.
4- Sinovac vaccine
: The vaccine contains corona virus inactivated by various chemical processes in the laboratory.
The shell of this virus remains intact, and during the injection, the immune system learns to recognize it and defend itself against the virus.
5- Sputnik
V vaccine: Similar to the AstraZeneca laboratory vaccine, the Russian vaccine uses the principle of a viral vector, and it uses two adenoviruses, responsible for common colds, and they have been genetically modified so that they do not multiply, and a gene has been combined Spike protein encoded in their genome.
6-
CanSino Biologics: a single dose vaccine, based on the viral vector technology.
7- Sinopharm vaccine
: The vaccine contains SARS-Cove-2 virus inactivated by different chemical processes in the laboratory.
The shell of this virus remains intact, and during the injection, the immune system learns to recognize and defend itself against the virus.
8- Johnson & Johnson
vaccine: a single dose vaccine, this vaccine uses a genetically modified adenovirus for the common cold to reduce its reproduction as a viral vector.
The SARS-Cove-2 spike protein gene is inserted into the genome of this viral vector.
Once injected, the virus enters human cells.
These cells then produce a spike protein, which allows the immune system to learn to recognize and fight SARS-CoV-2.
A deeper look at US vaccines
In an article published by the American "Business Insider" website, writer Aria Bendix said that it is normal to feel some discomfort after receiving an anti-Coronavirus vaccine.
Once the vaccine is injected into your arm, blood flow increases and immune cells rush to the site of the vaccination, and this can lead to pain at the injection site, which is the most common side effect of the three coronavirus vaccines licensed by the United States (Pfizer, Moderna, Johnson & Johnson) .
The author said that this interaction is more common with the Pfizer and Moderna vaccines compared to the Johnson & Johnson vaccine. Less than 50% of the participants in the clinical trials of the Johnson & Johnson vaccine reported pain at the injection site, compared to 92% for those who underwent the Moderna vaccine and 84% for the vaccine. Pfizer.
The author explained that when the immune system detects the components of the vaccine, it releases inflammatory chemicals to protect us.
Because of this, shortly after receiving the vaccine, a person can develop a fever, muscle pain, fatigue, or headache.
Fatigue was the second most common side effect in the clinical trials of Pfizer and Moderna.
About 69% of the participants in the Moderna vaccine trials and 63% of the participants in the Pfizer vaccine trials reported experiencing a state of fatigue.
Headache was more common than fatigue among participants in the Johnson & Johnson vaccine trials, with 39% reporting a headache, and 38% reporting fatigue.
Fatigue and headache are among the most common side effects after receiving the second dose.
Muscle pain
And in all clinical trials of the three vaccines, muscle pain was the fourth most common side effect.
In the trials of the Moderna vaccine, 60% of the participants experienced muscle pain, while 38% of the participants in the Pfizer vaccine trials reported the same symptoms, compared to about a third for the Johnson & Johnson vaccine.
The author stated that chills were less common, but not completely rare, as 43% of Moderna vaccine recipients reported feeling chills, while only 32% of participants in Pfizer vaccine trials reported this condition.
Only 2% of the participants in the Johnson & Johnson vaccine trials felt chills.
15% of the participants in clinical trials of the Pfizer and Moderna vaccines reported having a fever, compared to about 9% for the Johnson & Johnson vaccine.
The author confirmed that the recipients of the Pfizer and Moderna vaccines did not experience digestive problems such as nausea, vomiting and diarrhea, while about 14% of Johnson & Johnson vaccine recipients reported nausea.
The majority of the participants in the Moderna trials reported that side effects began on the day they received the vaccine and continued for two days after each dose.
On average, someone receiving a Pfizer vaccine experienced side effects one to two days after the vaccination, and the reaction usually lasted only one day.
The participants in the Johnson & Johnson vaccine trials had symptoms of fatigue, headache and muscle pain for an average of two days, while they experienced symptoms of nausea and fever for only one day.