Osaka Prefecture announced on the 6th that it has been confirmed that 719 people will be infected with the new coronavirus, which is the largest number ever.
This has surpassed the number of infected people in Tokyo for eight consecutive days, but one of the causes of the rapid spread of infection is the mutant virus.
In the Kansai region, many of the first types of mutant viruses found in the United Kingdom have been identified.
We asked experts about how they differ from conventional viruses and what to do about infection control.
Percentage of mutant viruses gradually increases
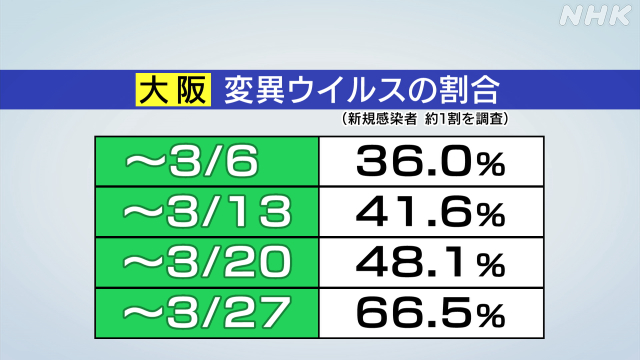
The proportion of people who have been confirmed to be infected with the mutant virus is gradually increasing.
Osaka Prefecture has been conducting screening tests since January to investigate the actual situation of the spread of the mutated new coronavirus.
Osaka Prefecture does not immediately indicate the overall status of the spread of the mutant virus, as the test targets include close contacts with the mutant virus, but the percentage continues to rise.
66.5% in the week until March 27th.
It is calculated that 2 out of 3 people who have been tested are infected with the mutant virus.
Infectivity is up to 1.7 times “British type”
The most common type of mutant virus found in the United Kingdom is the one found in the United Kingdom.
According to the WHO summary, this mutant virus is up to 1.7 times more infectious than the conventional type, which is considered to be one of the factors for the spread of infection.
There is a mutation called "N501Y" in this virus, and the protrusions on the surface that serve as a foothold for the virus to infect humans have changed to make it easier to infect, which makes it more infectious. It is being considered.
We will look at three points to see how mutant viruses differ from conventional types.
What is highly infectious?
What do you need to be aware of against mutant viruses?
It has been pointed out that strong infectivity means that even a small amount of virus can be transmitted, making it easier to infect at any age.
In particular, children are considered to be less susceptible to infection with the conventional type than with other age groups, but it is thought that mutant viruses will be infected in the same way as with other age groups.
Dr. Yoshinori Yasui of Osaka Saiseikai Nakatsu Hospital, who is familiar with infectious diseases, says that caution is required because the infection can easily spread among children.
(Dr. Yasui)
"Even if the virus is less than before, it will be transmitted. Outbreaks may occur between children and in facilities where outbreaks have rarely been seen. Schools, kindergartens, etc. There is a risk that it will spread to each family through the nursery school, and we must take further measures against infection in schools, kindergartens and nursery schools. "
What is the risk of aggravation and death?
The details of the risk of aggravation and death are not yet known.
However, according to WHO, there is a possibility that there is an increased risk of hospitalization, serious illness, and death.
Experts point out that it is necessary to collect and investigate cases of mutant viruses in the future.
What is the effect of the vaccine on mutant viruses?
I am very wondering if the vaccine is effective against mutant viruses.
According to the WHO, there is no significant change in the effectiveness of the vaccine for the first mutant virus reported in the United Kingdom.
Also, in Israel, a paper was published that the effect of preventing the onset of Pfizer's vaccine was 94% and the effect of preventing infection was 92%, and the mutant virus found in the United Kingdom during the period targeted for analysis was The epidemic suggests that it is effective against this mutant virus.
Vaccination of the elderly will begin on the 12th of this month, but it will take some time to reach the whole.
Experts point out that it is important to control explosive infections until the vaccine is widespread.
(Dr. Yoshinori Yasui, Nakatsu Hospital, Saiseikai, Osaka)
"I think we should think that the number of patients is still suppressed to this level because we are taking measures against infection. It will be stronger if the number of patients does not decrease. There may come a time when we have to take measures, such as restricting going out. I think the next month or two is very important. While controlling the rate of increase in infected people, we will increase the vaccination rate. It is important to give it up. "