The government is considering issuing a state of emergency as a countermeasure against the new coronavirus, which continues to spread.
As a result of a new simulation conducted by Professor Hiroshi Nishiura of Kyoto University, the end of February is expected to have the same level of effect as last year's state of emergency in order to sufficiently reduce the number of infected people in Tokyo. It turns out that it will take up to.
When the state of emergency was first declared in April last year, we specialize in the analysis of infectious diseases using mathematical models, and based on the simulation results of Professor Hiroshi Nishiura of Kyoto University, we should make as much contact as possible between people 8 It was called for a reduction.
Regarding the fact that the state of emergency is being considered again this time, Professor Nishiura once again simulated the future changes in the number of infected people in Tokyo.
The simulation was done using a number called the "effective reproduction number", which indicates how many people an infected person infects.
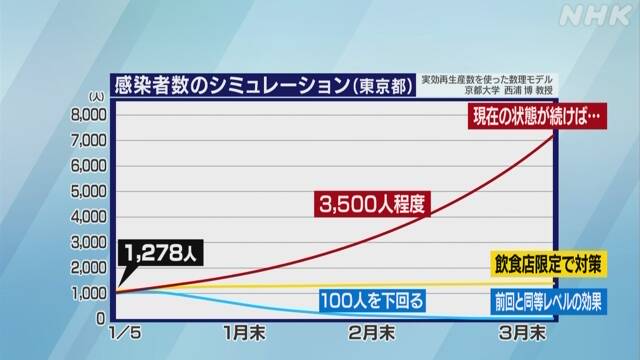
According to this, from the current infection situation, the effective reproduction number in Tokyo is about 1.1, and if this state continues without new measures, the number of new infections as of the end of February is about 3500 per day. The number of people is expected to increase to about 7,000 at the end of March.
Then, using a mathematical model, we calculated how much the number of infected people would be reduced by taking new measures with reference to the data from the first and second waves of the epidemic that we experienced last year.
As a result, if measures such as shortened business hours are taken only for restaurants, the number of effective reproductions is expected to decrease by 10% to 0.99, and in this state the number of newly infected people will almost decrease. As of the end of February, there were about 1,300 people a day.
On the other hand, if the effective reproduction number could be reduced to about 0.72, which is 35% less than now, it means that the number of newly infected people fell below 100 per day on February 25, a month and a half later.
The reduction of the effective reproduction number by 35% is the same level as the effect of the last April's state of emergency declaration, and if the effect is weaker than this, it will take a longer period until the number of infected people decreases. It means that it will take.
According to Professor Nishiura, in order to obtain the same level of effect as the previous state of emergency, while focusing on measures for restaurants, refraining from going out unnecessarily, refraining from moving across prefectural borders, thorough remote work and the company It means that it is necessary to take thorough measures to reduce the risk of infection, such as avoiding meetings in Japan.
Professor Nishiura, who conducted the simulation, said, "I think that it is possible to achieve sharp contact reduction by combining various measures, rather than refraining from society as a whole. Effectiveness is very important for issuing a state of emergency. And if it fails, not only psychological damage but also social and economic damage will be enormous. The country needs to take responsibility for measures to drastically reduce the number of infected people. " I'm talking to you.