Focus on it!
Announce the 14th Five-Year Plan for technological innovation in many places, aiming at these areas
During the "14th Five-Year Plan" period, scientific and technological innovation has been placed in an important position, and various regions have successively formulated specific construction drawings based on resource endowments.
According to incomplete statistics, Shanghai, Guangdong, Jiangsu, Hubei and other places have recently announced the 14th Five-Year Plan for technological innovation, clarifying the focus of construction in the next five years.
Three Science and Technology Innovation Centers: Strategic Science and Technology Power
China has basically formed a number of innovation clusters, namely the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei innovation cluster with Beijing as the center, the Yangtze River Delta innovation cluster with Shanghai as the center, the Pearl River Delta innovation cluster with Guangdong as the center, and Chengdu , Chongqing, Wuhan, and Xi’an are the regional innovation clusters.
The "14th Five-Year Plan" clearly states that Beijing, Shanghai, and the Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macao Greater Bay Area will be supported to form international scientific and technological innovation centers.
At the previous press conference of the State Council Information Office, Xu Wei, director of the Strategic Planning Department of the Ministry of Science and Technology, said that during the "14th Five-Year Plan" period, we must continue to support the construction of international science and technology innovation centers in Beijing, Shanghai, and the Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macao Greater Bay Area.
It is necessary to strengthen the layout of major national innovation bases and platforms, and focus on deepening the reform of the scientific and technological system and policy innovation.
In this regard, it is hoped that the three places can play a "leading goose" role in policy innovation, have more explorations, promote the benign interaction and organic integration of technology, industry, and finance, and take the lead in creating a source of scientific and technological innovation in China, forming a leading high-quality development. An important source of power.
At present, the medium and long-term plans of the three major science and technology centers have also been clarified. Among them, innovating sources and strengthening the national strategic scientific and technological strength are the key points of construction.
A few days ago, Shanghai announced the "Fourteenth Five-Year Plan for Shanghai to Build a Globally Influential Science and Technology Innovation Center."
In order to strengthen the source of scientific and technological innovation, the Shanghai Science and Technology Innovation Center will pay close attention to the implementation of 8 key tasks during the "14th Five-Year Plan" period.
The first thing is to accelerate the original breakthrough of basic research and enhance the original innovation ability.
For example, speed up the construction of Zhangjiang Comprehensive National Science Center, build a group of strategic scientific and technological forces, forward-looking deployment of a group of strategic and basic frontier projects, support universities, research institutes and enterprises to independently deploy basic research, and accelerate the formation of a group of basic research And apply the original results of basic research, achieve "from 0 to 1" original breakthroughs, and strive to become "the first discoverer of scientific laws."
"Basic research is the'power source' for the Shanghai Science and Technology Innovation Center to enhance the function of scientific and technological innovation." The Shanghai Research Group on Strengthening Mid- and Long-term Basic Science Forward-looking Deployment Strategic Research Group interprets the Shanghai plan.
At the press conference on planning interpretation held by the State Information Office, Li Meng, the vice minister of science and technology, said that strengthening strategic scientific and technological capabilities is a major task in the construction of the Shanghai Science and Technology Innovation Center.
During the "14th Five-Year Plan" period, the Ministry of Science and Technology will further support Shanghai in accelerating the construction of an international science and technology innovation center.
It will accelerate the construction of major scientific and technological innovation platforms to enhance Shanghai’s original innovation capabilities; promote Shanghai’s deep participation in the research and development of major national scientific and technological projects; strengthen the construction of a scientific and technological innovation community in the Yangtze River Delta with Shanghai as the leader, and create a new engine for future industries; support Shanghai’s deep integration into the world Innovation network; support Shanghai to gather high-end talents.
Shi Qian, director of the Shanghai Institute of Science, told CBN that it is not easy to innovate the source of the strategy, because the source of the strategy is accidental and requires a degree of concentration.
"All kinds of resource endowments, industrial chains, and innovation chains have a certain degree of concentration to produce results. Many places are promoting innovation sources, but Shanghai is the only city that regards innovation sources as the entire city function, not just The ability of technology."
Guangdong, which has the largest total GDP, announced the "Fourteenth Five-Year Plan for Scientific and Technological Innovation in Guangdong Province" in mid-to-early October. It is proposed that by 2025, Guangdong’s main innovation indicators will reach the international advanced level, and a higher level of technological innovation will be established. The Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macao Greater Bay Area has initially established a technological and industrial innovation highland with global influence and has become an important source of innovation power for the country.
When interpreting the plan, the Guangdong Provincial Department of Science and Technology stated that during the "14th Five-Year Plan" period, Guangdong's scientific and technological innovation will follow the "seven focus and seven efforts" to lay out key tasks.
Specifically, it includes focusing on major national needs and striving to strengthen strategic scientific and technological strength; focusing on the frontiers of world science and technology and striving to strengthen source innovation supply; focusing on the main economic battlefield and striving to improve support and leading capabilities; focusing on people's health and striving to serve the needs of a better life; Enterprise innovation capabilities, focus on strengthening the position of innovation main body; focus on the construction of talent team, focus on creating a highland of innovative talents; focus on system and mechanism reform, focus on promoting the modernization of innovation governance.
The plan formed 10 quantitative predictive indicators.
For example, regional innovation capabilities continue to rank first in the country, R&D expenditures have increased by an average annual rate of 10%, R&D/GDP has reached about 3.5%, and the full-time equivalent of R&D personnel per 10,000 people has reached 90 person-years.
Funds for basic research in the whole society accounted for 10% of R&D funding. There were 20 high-value invention patents per 10,000 people, and the cumulative number of overseas invention patents granted reached 80,000.
As one of the regions with the strongest scientific and technological foundation in China, Beijing’s goal is that by 2025, the Beijing International Science and Technology Innovation Center will be basically formed; The highland of talents effectively supports our country's construction of a powerful country in science and technology.
According to the "Fourteenth Five-Year Plan" Beijing International Science and Technology Innovation Center Construction Strategic Action Plan, strengthening the national strategic science and technology strength is an important part of the construction of Beijing International Science and Technology Innovation Center.
The strategic action plan proposes to accelerate the cultivation and construction of national laboratories, promote the systematic development of the state key laboratories in Beijing, accelerate the construction of a comprehensive national science center in Huairou, promote the construction of world-class major scientific and technological infrastructure clusters, and cultivate a new group of new research and development centering on advantageous areas mechanism.
At the press conference held in January, Li Meng introduced that the key to the construction of Beijing International Science and Technology Innovation Center is to build capacity and ecology.
The first is to deploy the national strategic scientific and technological forces to build traction; the second is to develop major basic frontier research and development to build originality; the third is to first try reforms and policies to build new power; the fourth is to stimulate talent innovation and creativity to build attractiveness; It builds influence based on all-round open cooperation in science and technology.
According to Dr. Zhang Mizhi, deputy director of the Statistical Evaluation Research Office of the Shanghai Institute of Science, the hierarchical system of the national scientific and technological innovation spatial layout during the 14th Five-Year Plan period has undergone certain changes in key construction areas and key tasks. It can be summed up as "highlight the core, move westward, and market first".
He told reporters that in terms of spatial layout, during the "14th Five-Year Plan" period, a number of international technological innovation centers with global influence will be built, becoming important benchmarks for China's participation in international technological innovation competition and cooperation, and supporting the construction of an innovative country.
It can be seen that the national strategic scientific and technological strength and major scientific and technological projects will still be inclined to these places, forming a new nationwide system for scientific and technological research to carry out cutting-edge scientific and technological exploration.
How does the regional innovation center do
In addition to the three major science and technology innovation centers in Beijing, Shanghai, Guangdong, Hong Kong and Macao, many other provinces with rich scientific and educational resources have also drawn up a roadmap for the development of scientific and technological innovation in the next five years.
The "14th Five-Year Plan" for scientific and technological innovation and development in Zhejiang Province proposes that by 2025, the construction of the three major scientific and technological innovation highlands will be accelerated, and a world-class "Internet +" technology innovation highland will be basically established, and a world-class life, health and new materials science will be initially established. Create high ground.
In addition, the plan also clarified that "do a good job of ten key points and form ten breakthroughs."
For example, in terms of fighting the battle for key core technologies and speeding up seizing the commanding heights of science and technology, we have sorted out and formed four lists such as applied research to force basic research, basic research to lead applied research, domestic substitution list, and achievement transformation list. The four major research plans of "Pioneer, Vanguard, Leading Goose, and Leading" have solved a batch of "stuck neck" problems and achieved 100 major achievements that fill the gaps and lead the future.
Jiangsu Province recently announced the "14th Five-Year" Science and Technology Innovation Plan, proposing that by 2025, the construction of a science and technology province has made important progress in stages, and basically built an industrial science and technology innovation center with global influence, and its main innovation indicators have reached innovative countries and regions. In the same period, the level was above average.
Jiangsu's plan has made a systematic design for the construction of a strong science and technology province, which mainly includes four aspects. It takes the fight for key core technologies as the primary task, the implementation of key scientific and technological innovation actions as the key means, and the creation of regional innovation and development growth poles as an important path , Regard accelerating the modernization of scientific and technological governance capabilities as a powerful driving force.
In addition, the work objectives of the Jiangsu Plan are mainly embodied in the "four powers", namely, strong independent innovation ability, strong leading and supporting role, strong innovation system coordination, and strong innovation and entrepreneurship ecology.
Specifically, including major breakthroughs in basic research and key core technologies, breaking through a number of major bottlenecks restricting economic and social development, forming first-mover advantages in a number of strategically contested areas, and total R&D investment in the entire society as a proportion of the regional GDP 3.2%; the output value of high-tech industries accounts for about 50% of the total output value of industries above designated size.
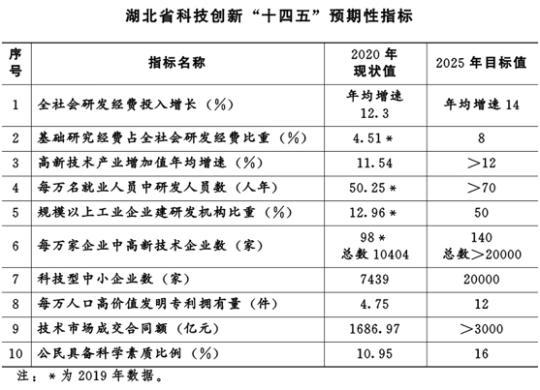
Hubei, a major science and education province in central China, also proposed that by 2025, it will basically become a science and technology province, rank among the top of the country's innovative provinces, form a leading position in the national science and technology innovation map, and strive to lead the country in innovation-driven development and become a leader in the central region. The rising scientific and technological innovation fulcrum, the technological innovation center with national influence and the important link of the global innovation network.
According to the "14th Five-Year Plan for Science and Technology Innovation in Hubei Province", Hubei has made it clear that during the "14th Five-Year Plan" period, the average annual growth rate of R&D investment in the whole society will reach 14%, and the average annual growth rate of the added value of high-tech industries will reach over 12%. By 2025, basic research funding will account for 8% of the total social R&D funding, and the number of R&D personnel per 10,000 employees will exceed 70 person-years.
Multi-regional efforts in scientific and technological innovation have further coordinated the regional innovation pattern.
Statistics released by the Bureau of Statistics on September 22 show that in 2020, R&D expenditures in China's eastern, central, and western regions will be 165.173 billion yuan, 466.29 billion yuan, and 321.29 billion yuan, respectively, an increase of 9.2%, 12.0%, and 12.4% over the previous year. , The growth rate of the central and western regions exceeded that of the eastern region for 4 consecutive years.
In addition, the 2021 Global Innovation Index (GII) released by the World Intellectual Property Organization (WIPO) in September also shows that China has nearly one-fifth of the world's leading technology clusters, and the ranking of most clusters has risen significantly.
Zhang Mizhi said: "In the GII's regional sector this year, the leading role of Guangdong, Hong Kong, Macao, Beijing, and Shanghai International Science and Technology Innovation Centers has been continuously highlighted. At the same time, the rankings of most Chinese science and technology clusters have been improved. This is in line with the current echelon formed in China. An orderly regional innovation development layout is inseparable. The central and western regions have become an important force for China’s future scientific and technological innovation. Based on the construction of international scientific and technological innovation centers in Beijing, Shanghai, and the Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macao Greater Bay Area, we will guide innovation resources to gather in the central and western regions. A key measure for technological innovation to promote coordinated regional development.” (Author: Jin Yezi)