RMB loans increased by 1.08 trillion yuan in July
Financial support for the real economy continues unabated, our reporter Yao Jin
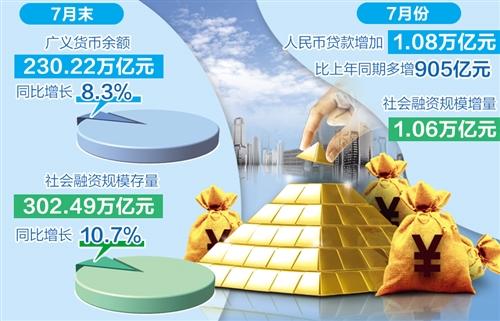
On August 11, the financial statistics report released by the People’s Bank of China showed that at the end of July, the balance of broad money (M2) was 230.22 trillion yuan, a year-on-year increase of 8.3%, and the growth rate was 0.3 and 2.4 lower than the end of the previous month and the same period of the previous year. In July, RMB loans increased by 1.08 trillion yuan, an increase of 90.5 billion yuan over the same period last year, and the increase in social financing was 1.06 trillion yuan, which was 636.2 billion yuan less than the same period last year.
"Increased fiscal return has led to a decline in the growth rate of M2." Wen Bin, chief researcher of China Minsheng Bank, said that July was the traditional month for tax payment. Fiscal deposits increased by 600.8 billion yuan, an increase of 113.6 billion yuan over the same period last year. With the increase in currency withdrawal, the growth rate of M2 has fallen.
China Everbright Bank analyst Zhou Maohua also believes that the decline in M2 growth is essentially due to a slowdown in deposits.
July is the big month for tax payment, and the corresponding deposits of individuals and companies will decline after tax payment. At the same time, the domestic credit environment has tightened, economic activities have slowed down, and the investment and financing activities of enterprises and individuals have declined, as well as off-balance sheet business activities of banks. Continued contraction will affect the ability to derive currency.
Overall, the year-on-year growth rate of M2 is still in a reasonable range (the year-on-year growth rate of M2 basically matches the growth rate of nominal GDP).
The new loan structure reflects the weakening of financing demand in the real economy.
Wen Bin believes that the decline in new loans for the residential sector is mainly due to the recent real estate control policies that continue to upgrade and increase, severely crack down on the illegal use of short-term loans, and mortgage loan lines are also under control.
The enterprise sector’s new loans were 433.4 billion yuan, an increase of 168.9 billion yuan over the same period last year, but the structure has deteriorated.
The newly-increased scale of medium and long-term loans to enterprises was only 493.7 billion yuan, an increase of 103.1 billion yuan compared with the same period last year, which was the second lowest new scale since the outbreak of the epidemic (411.3 billion yuan in October last year).
Short-term loans to enterprises decreased by 257.7 billion yuan, an increase of 15.6 billion yuan over the same period last year, but bill financing increased by 177.1 billion yuan, an increase of 279.2 billion yuan over the same period last year.
In terms of social finance, the increase in social financing in July was 1.06 trillion yuan, 636.2 billion yuan less than the same period last year; the stock of social financing at the end of July was 302.49 trillion yuan, a year-on-year increase of 10.7%, a decrease of 0.3 percentage points from the previous month , Which is the lowest since the epidemic last year.
“New social financing is lower than expected, and the non-standard pressure drop and slow issuance of government bonds are the main reasons.” Wen Bin said, first, under the policy of preventing risks, shadow banking and off-balance sheet business governance continue to be strict. Foreign financing continued to show a downward trend. In July, entrusted loans, trust loans, and undiscounted bank acceptances decreased by 15.1 billion yuan, 157.1 billion yuan, and 231.6 billion yuan, respectively, a decrease of 100 million yuan and an increase of 20.4 billion yuan from the same period last year. And 118.6 billion yuan.
Second, the new government bonds were not as expected. The issuance of government bonds this year was significantly slower than in previous years. In July, government bond financing was only 182 billion yuan, an increase of 363.9 billion yuan from the same period last year.
Third, new on-balance sheet loans (RMB + foreign currency loans) have also fallen. In July, new on-balance sheet loans were 831.3 billion yuan, an increase of 138.4 billion yuan from the same period last year.
In addition, small fluctuations in direct financing (corporate bonds + stocks) have little impact on the overall decline in social financing.
Zhou Maohua said that the July social financial credit data was less than expected, reflecting the slight cooling of domestic economic activities, which was mainly affected by several factors: First, the rise in commodity prices has caused some midstream and downstream enterprises to temporarily wait and see. A further decline in PMI can be seen; second, domestic real estate regulation has become stricter, and residents' mid- and long-term loans have declined significantly; third, emergencies such as epidemics and extreme weather have restrained domestic economic activities.
"It is necessary to closely observe the changes in the financing needs of the real economy." Wen Bin believes that the scale of new loans is more than the level of the same period last year, reflecting the financial support of the real economy, but the new loan structure reflects the weakening of the financing needs of the real economy.
Social financing is in the process of building a bottom. The decline in social financing reflects the general trend of governing off-balance-sheet financing. Government bond financing is obviously weak. It is expected to accelerate the issuance of government bonds, which will support the growth of social financing; but the base of social financing last year Gradually higher, it also means that the next stage of social financial growth is likely to maintain low fluctuations.
Macroeconomic policies should adhere to the principle of stability, do a good job in cross-cycle policy design, maintain reasonable and sufficient liquidity, and increase support for key areas and weak links such as manufacturing, small, medium and micro enterprises, inclusive finance, green finance, and technological innovation.
China Postal Savings Bank researcher Lou Feipeng believes that since the beginning of this year, the domestic prudent monetary policy has been flexible, precise, reasonable and appropriate, keeping the growth rate of money supply and social financing scale basically matching the nominal economic growth rate, effectively serving the continuous recovery of the real economy. From the perspective of money supply, in the context of sustained economic recovery, the year-on-year growth rate of M2 and M1 in July was significantly lower than last year. Based on this, it can be seen that there has been no flooding. From the perspective of the scale of social financing, as off-balance sheet financing such as entrusted loans, trust loans, and undiscounted bank acceptances continues to drop, the proportion of loans in the scale of social financing increased by 1% year-on-year, which also shows that finance is strongly supporting The real economy.